Figure 1.
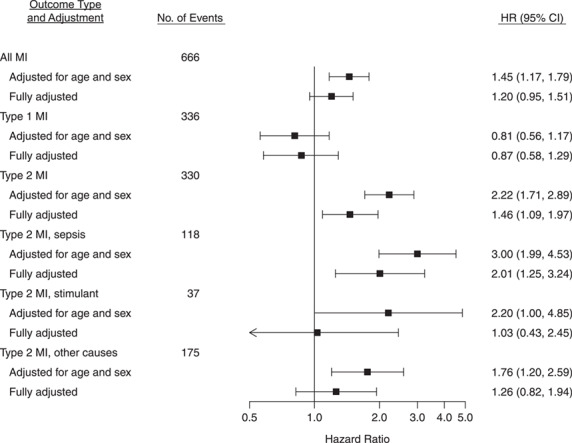
Hazard ratios (HRs) for the association between chronic hepatitis C virus infection and myocardial infarction (MI) outcomes among adults living with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) at 6 sites in the CFAR Network of Integrated Clinical Systems, United States, 1998–2016. Fully adjusted models took into account age, sex at birth, race/ethnicity, study site, men who had sex with men, ever smoking, history of injecting drug use, diabetes status, statin use, hypertension, antihypertensive medication use, hepatitis B virus infection, antiretroviral therapy, CD4-positive cell count nadir, HIV viral load, body mass index, total cholesterol level, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol level, and triglyceride level. Bars, 95% confidence intervals (CIs). AIDS, acquired immunodeficiency syndrome; CFAR, Centers for AIDS Research.
