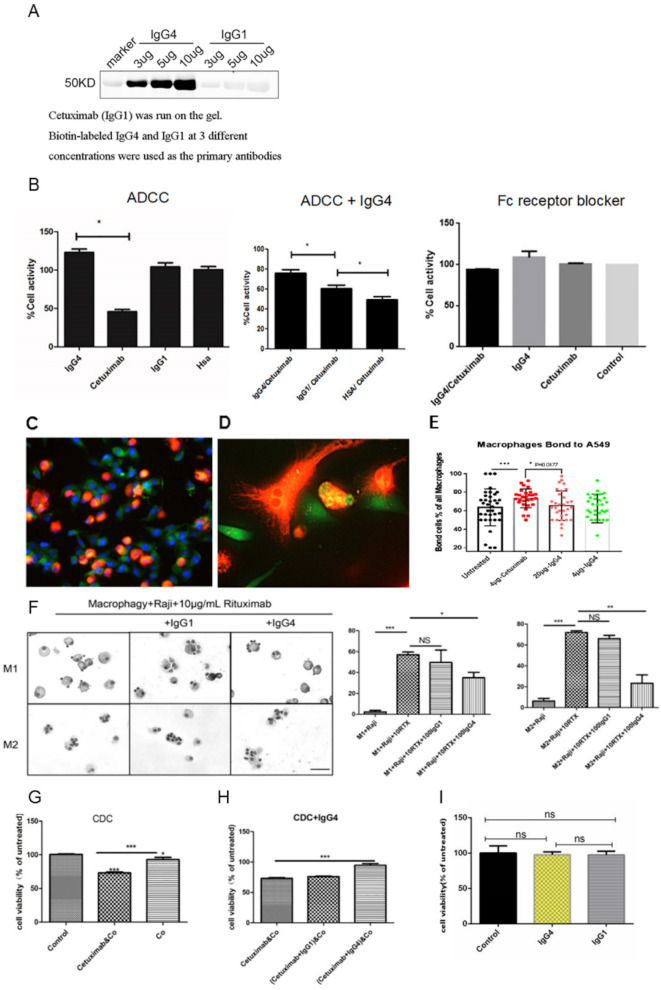
Figure 4.
Non-cancer-specific IgG4 inhibited classic ADCC, ADCP and CDC reactions against cancer but had no direct effect on cancer cell growth. (A) On western blot, the chimeric antibody cetuximab (IgG1 against EGFR) was run on the gel, and IgG4 and IgG1 at concentrations of 3, 5 and 10 µg/mL were used as the primary antibodies. IgG4 reacted to cetuximab at a concentration-dependent manner, but IgG1 did not react. (B) Left: In a classic ADCC experiment, cetuximab (IgG1) was incubated with an EGFR-expressing lung cancer cell line (A549) and then with PBMC from normal healthy adult. Cancer cell activity was significantly reduced (n=12). Non-cancer-specific IgG1 and HSA were used as controls showing that they had no direct effect on the cancer cells (n=12). Middle: When non-cancer-specific IgG4 was added to the mixture, the effect of cetuximab was significantly reversed demonstrating an inhibitory effect of IgG4 in ADCC (n=12). Non-cancer-specific IgG1 had a much smaller, but also significant, effect in inhibiting ADCC action (n=12). Right: When Fc receptor blocker was incubated with PBMC, the effect of cytotoxicity was blocked. (C–E) ADCP was performed with a lung cancer cell line A549 (expressing EGFR) as the targets, human peripheral monocyte-derived macrophages as the effector cells and the antibody cetuximab (IgG1) against EGFR as the mediating antibody. The tumor cells were stained with CFDA-SE fluorescence probes (green). Macrophages derived from PBMC were stained with DiI fluorescent probes (orange). Blue fluorescence is the nuclei stained with DAPI. (D) Higher magnification of (C). The orange-colored macrophages were in close contact with green tumor cells. Tumor debris ingested by macrophages appeared yellow in the cytoplasm of macrophages. (E) Bar chart showing the effect of ADCP and its inhibition by IgG4. (F) Left: In 10 µg/mL rituximab-mediated ADCP model, Giemsa staining results of phagocytosis of Raji cells by macrophages after the addition of 100 µg/mL IgG1 and IgG4, respectively. Right: IgG4 significantly inhibited rituximab-mediated ADCP in phagocytosis by macrophage, but IgG1 could not inhibit the ADCP effect. Scale bar=30 µm (*p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001). (G) In a classic CDC experiment, cetuximab anti-EGFR antibody was incubated with an EGFR-expressing lung cancer cell line (A549) and then with complement (Co) from serum of a normal healthy adult. The cancer cell activity was significantly reduced. (H) When non-cancer-specific IgG4 was added to the mixture in the above CDC experiment, the effect of cetuximab was significantly reversed. (I) IgG4 and IgG1 were incubated with KYSE150 for 24 hours and no effect on cell growth was found. ADCC, antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity; ADCP, antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis; CDC, complement-dependent cytotoxicity; CFSE-DA, carboxyfluorescein diacetate succinimidyl ester; DAPI, 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; HSA, human serum albumin; PBMC, peripheral blood mononuclear cell.