Figure 6.
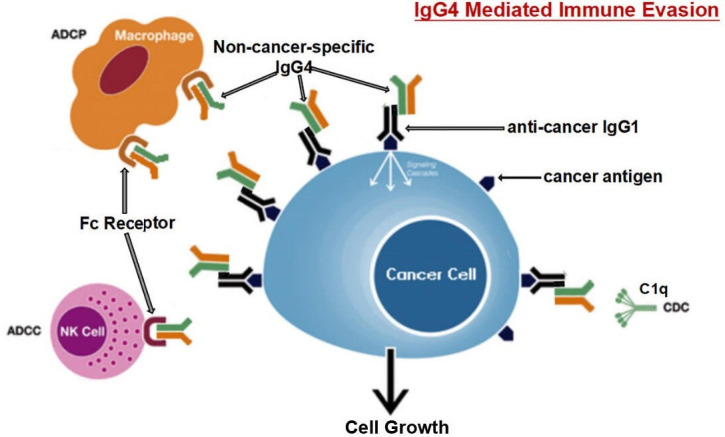
Diagrammatic illustration of proposed mechanism of cancer-initiated B lymphocyte-derived IgG4-mediated immune evasion. Chronic stimulation by cancer antigens induces class switch of B lymphocytes to produce IgG4. Such increased IgG4 can react to cancer-bound IgG with its Fc-Fc binding property and also to Fc receptors of immune effector cells. With its unique structural and biological property, increased IgG4 in cancer microenvironment mediates an effective immune escape for cancer. ADCC, antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity; ADCP, antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis; CDC, complement-dependent cytotoxicity; NK, natural killer cells.
