FIGURE 5.
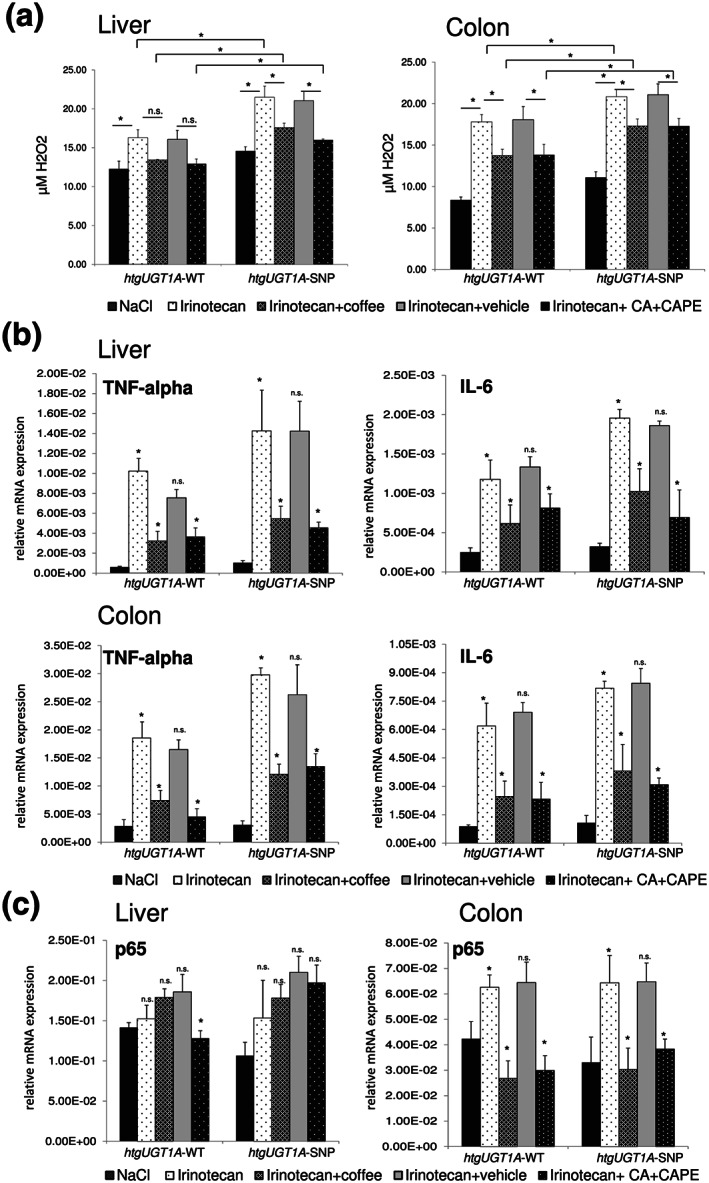
Protective effects of coffee and caffeic acid (CA) + caffeic acid phenylethyl ester (CAPE) pretreatment on irinotecan‐induced oxidative stress, inflammatory response and p65 up‐regulation. (a) Pretreatment with coffee and CA + CAPE led to a significant reduction of hydrogen peroxide levels in the liver and in the colon. Significance was determined as indicated by lines. Columns represent mean ± SD from five individual mice per group. Significance was determined as indicated by lines. (b) Irinotecan‐induced up‐regulation of TNFα and IL‐6 was significantly decreased in the liver and the colon of htgUGT1A‐WT and single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) mice. (c) In the colon, pretreatment with coffee and CA + CAPE abolished the irinotecan‐induced up‐regulation of p65 expression in htgUGT1A‐WT and single nucleotide polymorphism SNP mice. Columns represent mean ± SD from five individual mice per group (b,c). Significance of irinotecan group was determined in comparison to NaCl group; coffee group was compared to irinotecan group; CA + CAPE group was compared to irinotecan + vehicle group (b,c). *P < 0.05; n.s., non‐significant
