Figure 1.
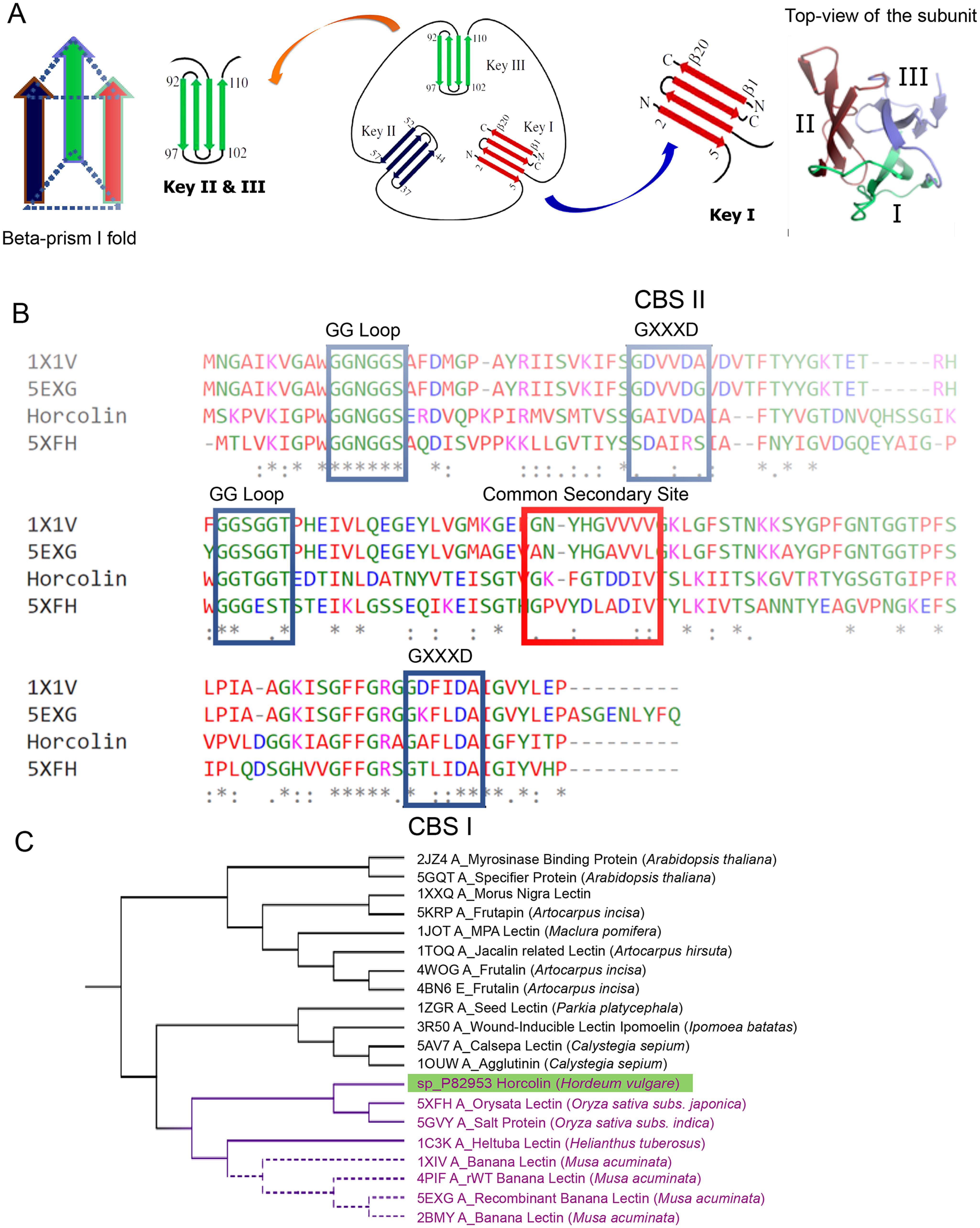
Homolog identification and bioinformatic analysis of horcolin. A, schematic representation of the jacalin fold indicating the four-stranded Greek key motif. Each monomer of the jacalin-related lectin is shown in a 3-fold axis with three Greek keys represented in different colors. B, multiple-sequence alignment of relevant mJRL homologs. The alignment of horcolin, BanLec, and orysata was obtained using Clustal Omega. The residues involved in mannose binding in CBS I and II are highlighted in blue, and the residues in the common secondary site are highlighted in red. C, molecular phylogenetic analysis by the maximum likelihood method. Horcolin was found to lie in the same clade as BanLec and orysata lectin, highlighted in purple.
