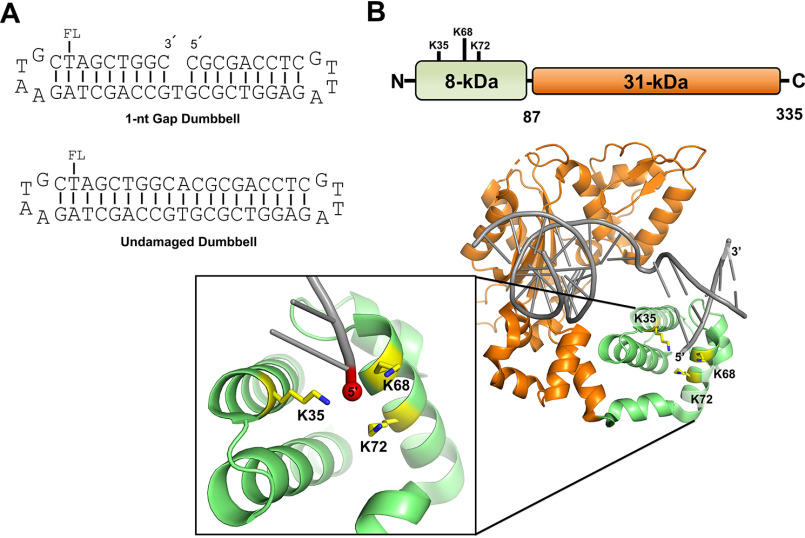
Figure 1.
A, representation of the DNA substrates used in this study. Substrates contain a fluorescein moiety (FL) covalently attached to the designated thymine base. The 1-nt-gap dumbbell DNA substrate (used to evaluate specific binding) contains a 5´-phosphate (not shown). The undamaged DNA substrate (used to evaluate nonspecific binding) was produced as described in Materials and methods. B, cartoon schematic of the DNA pol β domain organization (top) and the crystal structure of pol β bound to 1-nt-gap DNA (PDB entry 3isb). DNA pol β comprises two domains: the 8-kDa (8K) N-terminal dRP lyase domain, which catalyzes 5´-dRP removal, and the 31-kDa (31K) polymerase domain, which catalyzes gap-filling DNA polymerization during BER. The pol β mutations in the 8K lyase domain studied here, K35, K68, and K72, are illustrated; these lysine side chains are proximal to the 5´-phosphate in the 1-nt-gap.