Fig. 1.
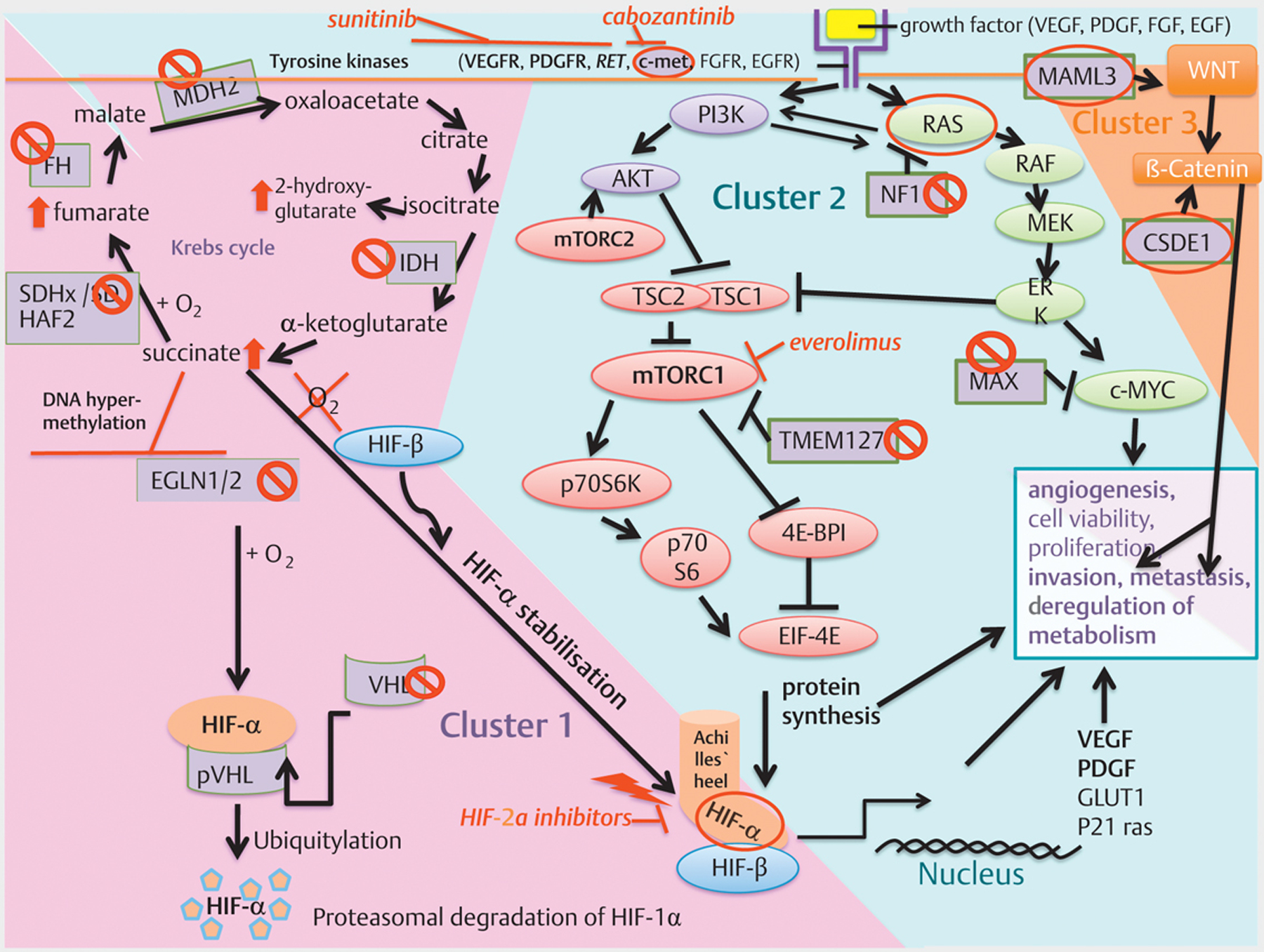
(modified from [17] and [103]) Overview: Cluster-1, −2 and −3 with molecular-targeted therapeutic options: Cluster-1: The pseudohypoxic signalling cluster includes mutations in genes encoding for hypoxia-inducible factor 2 alpha (HIF2A), Krebs-Cycle enzymes such as succinate dehydrogenase subunits (SDHx [SDHA, SDHB, SDHC, SDHD]), succinate dehydrogenase complex assembly factor 2 (SDHAF2), fumarate hydratase (FH), malate dehydrogenase 2 (MDH2), and isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH), moreover, von Hippel–Lindau tumour suppressor (VHL) and egl-9 prolyl hydroxylase 1 and 2 (EGLN1/2). SDH(A[AF2]/B/C/D), FH, MDH2 and IDH mutations impair the Krebs cycle and lead to an increase in succinate, fumarate, or 2-hydroxyglutarate. The accumulation of oncometobolites promote DNA hypermethylation and inactivate tumour suppressor genes, including egl-9 prolyl hydroxylase 1/2 (EGLN1/2). The impaired activity of EGLN1/2 leads less ubiquitination/degradation of HIF-α. The HIF-α degradation is VHL-dependent; Therefore, these mutations promote HIF-α stabilisation independent of hypoxia resulting in increased angiogenesis (VEGF/PDGF transcription amongst others), dysregulation of metabolism, migration, invasion and finally metastases. HIF-α is the common final point, the “Achilles’ heel”, of cluster-1 mutations, interconnecting cluster-1 with cluster-2 mutations. Cluster-2: The kinase signalling cluster comprises mutations in the RET proto-oncogene, NF1 tumour suppressor, H-RAS and K-RAS proto-oncogenes, TMEM127 and MAX. Receptor tyrosine kinases (amongst others RET, VEGFR, c-met) activate PI3K. PI3K activates AKT, which inhibits TSC1/2 leading to disinhibition/activation of mTORC1; mTORC1 phosphorylates and activates various proteins including p70S6K, by which p70S6 is phosphorylated. Activated p70S6 promotes cell growth, proliferation, cell survival, and leads amongst others to protein synthesis of HIF-1α, which favours angiogenesis (VEGF/PDGF transcription amongst others), invasion and metastasis under hypoxic or pseudohypoxic conditions in the case of SDHx-mutations. The RAS/RAF/ERK-pathway is also activated by tyrosine kinases (amongst others RET) and activates mTORC1. NF1 mutations lead to disinhibiton/activation of RAS. TMEM127 mutations lead to disinhibition/activation of mTORC1. The tumour suppressor MAX antagonises Myc-dependent cell survival, proliferation and angiogenesis: mutations lead to increased cell proliferation and angiogenesis. Cluster-3: The Wnt signalling cluster comprises somatic mutations in CSDE1 and the mastermind like transcriptional coactivator 3 (MAML3) fusion genes. MAML3 mutated PGLs/PCCs show hypomethylation and over-activation of Wnt signalling. CSDE1 mutations lead to over-activation of β-catenin, a taget of Wnt signalling. Over-activation of Wnt/β-catenin signalling favors tumour proliferation, invasion and metastases. ⦸Phaeochromocytoma promoting loss of function mutation of a tumour suppressor gene.  Phaeochromocytoma promoting gain of function mutation of a proto-oncogene. ⬆Increase/up-regulation in the case of cluster-1 mutations of the Krebs cycle enzymes. ⟘
Phaeochromocytoma promoting gain of function mutation of a proto-oncogene. ⬆Increase/up-regulation in the case of cluster-1 mutations of the Krebs cycle enzymes. ⟘ Inhibition. ↘Activation.
Inhibition. ↘Activation.
