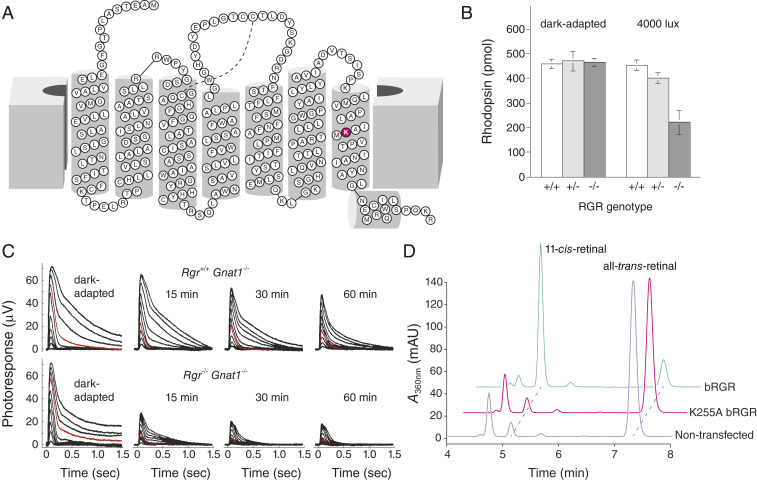
Fig. 4.
Evidence for RGR in supporting light-driven visual chromophore production. (A) A two-dimensional topology diagram showing the heptahelical structure of human RGR. The retinal binding Lys residue is highlighted in magenta. This research was originally published in the Journal of Biological Chemistry, ref. 77. © the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. (B) RGR helps maintain visual pigment levels in the setting of intense (4,000 lx) light exposure. Reprinted by permission from ref. 75, Springer Nature: Nature Genetics, copyright (2001). (C) Electrophysiological data documenting a role for RGR in the maintenance of cone photoreceptor responses during exposure to light. Reprinted from ref. 76. Copyright (2019), with permission from Elsevier. (D) Recombinantly expressed and purified RGR directly photoisomerizes all-trans-retinal to 11-cis-retinal upon exposure to 530-nm light. The activity depends on the presence of the Lys255 nucleophile to form a Schiff base conjugate with retinal, where bRGR means bovine RGR, A360nm, absorbance at 360 nm, and mAU, milli-absorbance unit. This research was originally published in the Journal of Biological Chemistry, ref. 77. © the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology.