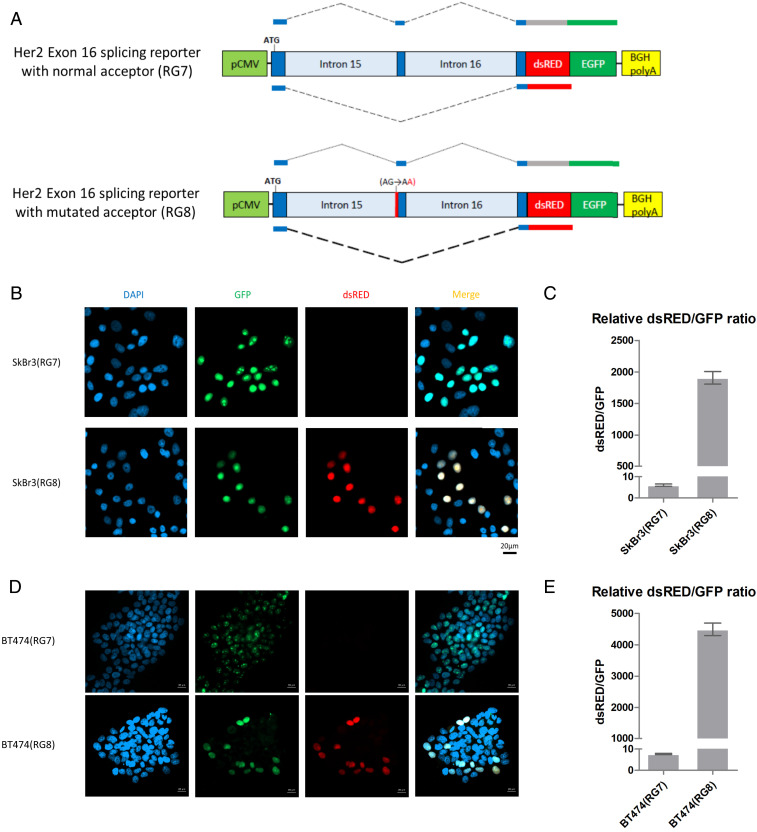
Fig. 3.
Mutation of the splice acceptor site at the ERBB2 intron15/exon16 junction leads to skipping of exon 16. (A) Schematic diagram illustrating the ERBB2 splicing reporter construct. In this system, inclusion of exon 16 will result in expression of GFP whereas skipping of exon 16 will result in expression of dsRed. Reporters were constructed with a wild-type splice acceptor site between intron 15 and exon 16 (RG7, Top) and containing the G-A mutation in the splice acceptor site (RG8, Bottom) that was identified in five human cancers (Fig. 2B). (B–E) SkBr3 (B and C) or BT474 (D and E) cells were transfected with the splicing reporter constructs, GFP and dsRed fluorescence was observed using confocal microscopy, and corresponding transcripts were quantified using qRT-PCR.