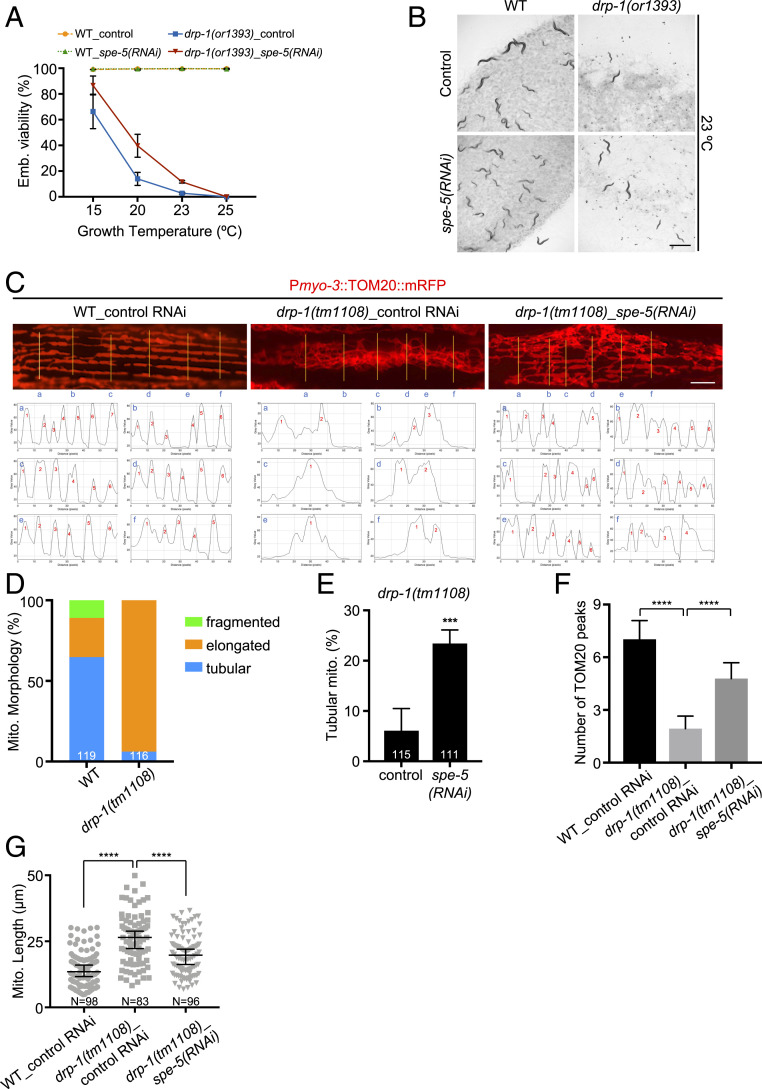
Fig. 1.
Inactivation of the vacuolar ATPase spe-5 suppresses drp-1 lethality and mitochondrial fission defects. (A and B) Viability of wild-type (WT) and drp-1(or1393) in control versus spe-5(RNAi) at indicated temperatures. Mean ± SD from at least three biological replicates. n = 80∼120 for each data point. (Scale bar, 1 mm.) (C) Mitochondrial morphology of wild-type and drp-1(tm1108) in control versus spe-5(RNAi) in a single body wall muscle cell. Mitochondria are visualized by a mitochondrial outer membrane localized mRFP fusion protein. (Lower) Plot profiles of the cross sections indicated by yellow lines. Criterion for a peak: Peak to trough (both sides) > 20 gray value units (y units). (Scale bar, 5 μm.) (D) Percentage of mitochondria with fragmented, elongated or tubular morphology in wild-type and drp-1(tm1108) in body wall muscles. The total numbers of mitochondria observed are indicated at the bottom of each bar. (E) Percentage of mitochondria with tubular morphology in drp-1(tm1108) body wall muscles after indicated RNAi treatments. The total numbers of mitochondria observed are indicated at the bottom of each bar. Mean ± SD ***P < 0.001. (F) Peak numbers for the plot profiles of mitochondrial morphology in indicated animals. Mean ± SD ****P < 0.0001. n = 40∼50 for each group. (G) Mitochondrial lengths in body wall muscles in indicated animals. Mitochondrial lengths were calculated by MiNA toolset. Median with 95% CI Mann–Whitney U test. ****P < 0.0001. N indicates the sample size.