Figure 3.
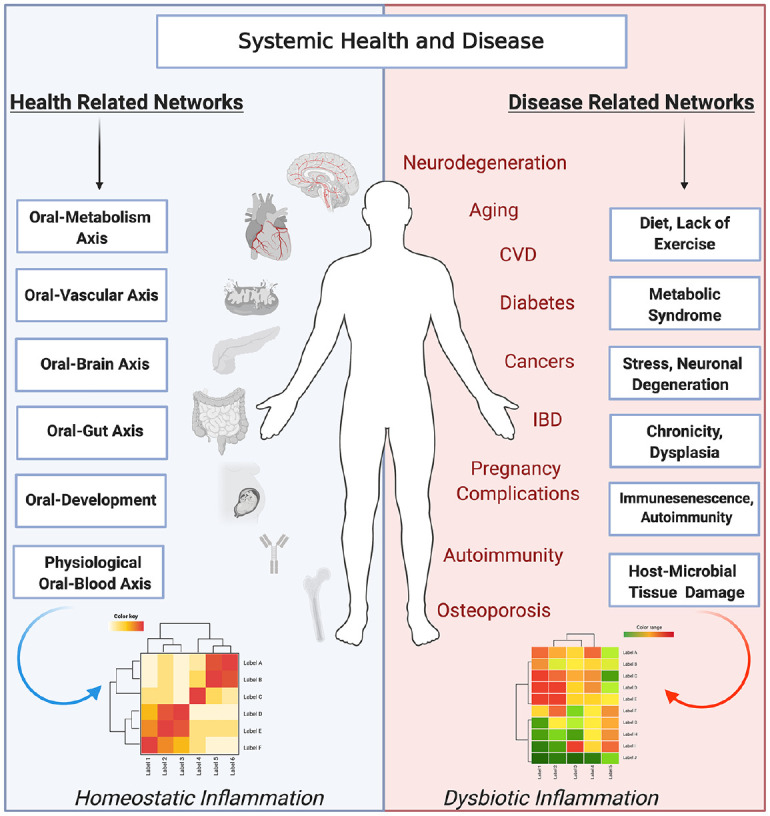
Dynamic interactions of the oral microbiome and host inflammatory networks play a role in oral dysbiosis and the oral impact on systemic diseases. The oral microbiome plays a key role in health and systemic disease. In a healthy state, homeostatic interactions of systemic and oral tissues lead to health. These driving factors affect systemic health through the oral-metabolism, oral-vascular, oral-brain, oral-gut, oral-development, and oral-blood axes. In contrast, oral dysbiosis can act through these axes to activate pathologic inflammatory networks, leading to chronic inflammation and, in conjunction with environmental factors, affecting systemic organs and aggravating systemic diseases, including diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, autoimmune diseases, age-related ailments, lung diseases, cancers, osteoporosis, pregnancy complications, and neurodegenerative diseases. Image created with BioRender.com. CVD, cardiovascular disease; IBD, inflammatory bowel disease.
