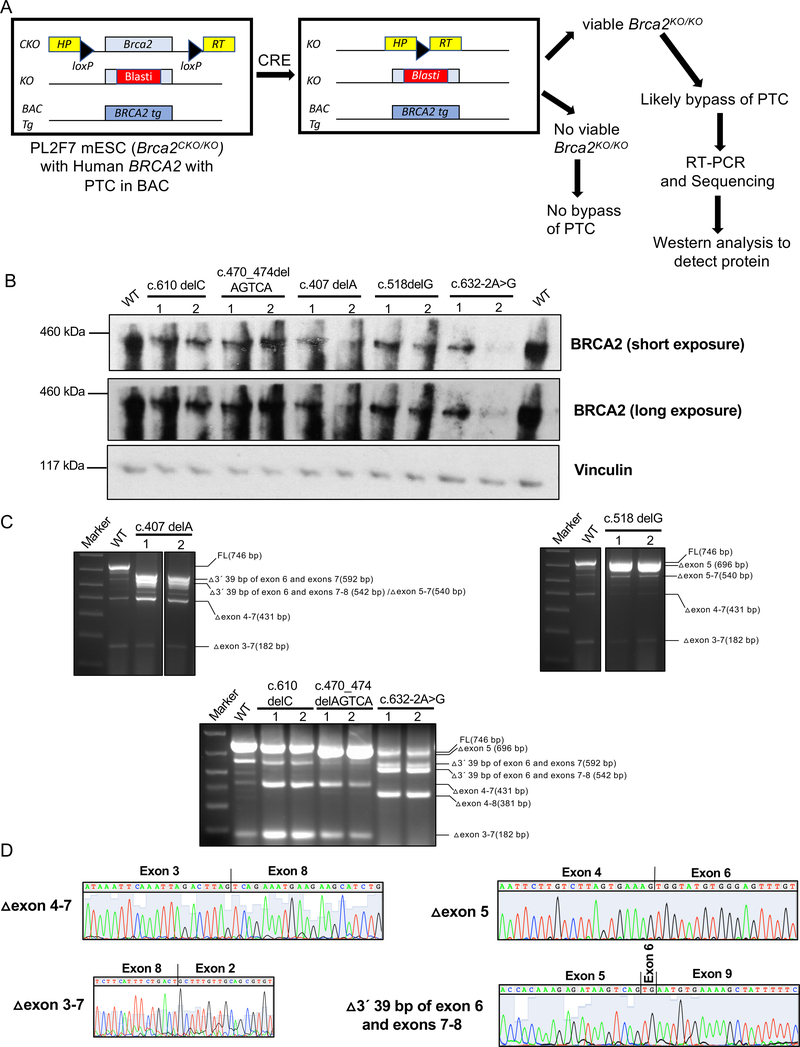
Figure 1: Functional evaluation of BRCA2 variants in mouse ES cells.
A. Overview of the ES cell-based functional assay where mutations are expressed in mESC containing a null allele (KO) and a conditional allele (CKO) of Brca2, which is flanked by two loxP sites containing the 5´ and 3´ halves of human HPRT minigene. Upon Cre expression the conditional allele is deleted and generates a functional HPRT minigene. Recombinant clones are selected in the presence of hypoxanthine-aminopterin-thymidine (HAT). In the absence of a functional BRCA2, such cells are not viable. Viable clones were further evaluated by RT-PCR and Western blot analysis.
B. Western blot analysis of Brca2KO/KO mESC showing expression of full-length protein by variants with a premature stop codon.
C. RT-PCR analysis to identify transcripts responsible for viability of Brca2KO/KO mESC expressing BRCA2 mutant alleles predicted to result in premature protein truncation. Primers used for RT-PCR are 5’GACACGCTGCAACAAAGCA3’ (exon 2)and 5’CATGACTTGCAGCTTCTCTTTGA3’ (exon 9).
D. Chromatogram of alternatively spliced transcripts that are predicted to encode functional BRCA2.