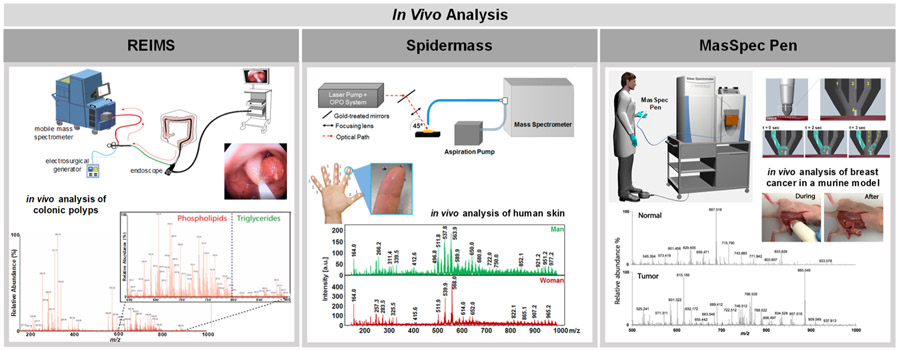
Figure 4.
Highlights of in vivo analysis using ambient ionization MS techniques. The left panel shows the use of an endoscopic version of REIMS termed iEndoscope for the analysis of colonic polyps. REIMS desorbs and ionizes molecules using an electrocautery device. A scheme of the endoscopic version of REIMS is shown at the top of the panel while a mass spectrum collected during the analysis of colonic polyps is shown below. Reprinted from Alexander, J.; Gildea, L.; Balog, J.; Speller, A.; McKenzie, J.; Muirhead, L.; Scott, A.; Kontovounisios, C.; Rasheed, S.; Teare, J.; Hoare, J.; Veselkov, K.; Goldin, R.; Tekkis, P.; Darzi, A.; Nicolson, J.; Kinross, J.; Takats, K. Surg. Endosc. 2017, 31, 1361–1370 (ref 86), with permissions from Springer. The center panel shows the use of SpiderMass, a device that utilizes resonant IR laser ablation to generate and desorb ions, in the analysis of human skin. A scheme of the device is shown at the top while mass spectra corresponding to the analysis of human skin of men and women are shown below. Adapted with permission from Scientific Reports, Fatou, B.; Saudemont, P.; Leblanc, E.; Vinatier, D.; Mesdag, V.; Wisztorski, M.; Focsa, C.; Salzet, M.; Fournier, I. Sci. Rep. 6, 2016 (ref 75). The right panel shows the use of the MasSpec Pen, a liquid extraction based method that uses a water droplet to nondestructively desorb diagnostic molecules from a tissue’s surface. A scheme of the MasSpec Pen is shown at the top of the panel, while mass spectra collected in vivo during tumor resection of breast cancer in a mouse model are shown below. Reproduced from Zhang, J.; Rector, J.; Lin, J. Q.; Young, J. H.; Sans, M.; Katta, N.; Giese, N.; Yu, W.; Nagi, C.; Suliburk, J.; Liu, J.; Bensussan, A.; DeHoog, R. J.; Garza, K. Y.; Ludolph, B.; Sorace, A. G.; Syed, A.; Zahedivash, A.; Milner, T. E.; Eberlin, L. S., Sci. Transl. Med., 9, 2017 (ref 40), with permission from the American Association for the Advancement of Science.