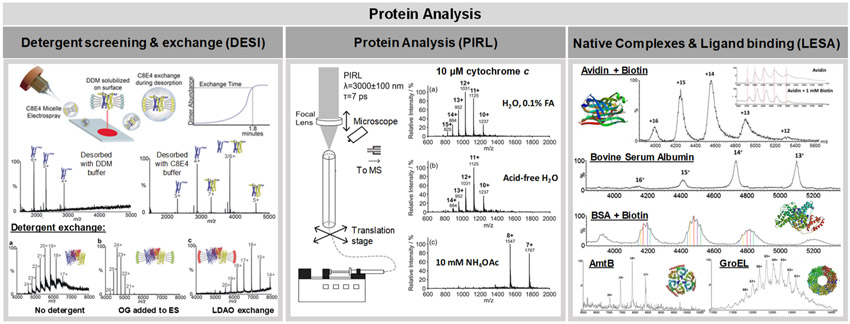
Figure 5.
Recent applications of ambient ionization MS for protein analysis. The left panel demonstrates the use of detergent additives in DESI-MS solvent to obtain native mass spectra of lipophilic proteins. Reproduced from Native Desorption Electrospray Ionization Liberates Soluble and Membrane Protein Complexes from Surfaces, Ambrose, S.; Housden, N. G.; Gupta, K.; Fan, J.; White, P.; Yen, H.; Marcoux, J.; Kleanthous, C.; Hopper, J. T. S.; Robinson, C.V. Angew. Che. Int. Ed. Engl., Vol. 56 (ref 146). Copyright 2017 Wiley. The center panel shows a schematic of PIRL for protein analysis. A variety of different protein charge states were observed for cytochrome c, including potentially native species. Modified from Lu, Y.; Pieterse, C. L.; Robertson, W. D.; Miller, R. J. D. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 4422–4428 (ref 149). Copyright 2018 American Chemical Society. The right panel shows LESA-MS analysis of a range of native protein complexes as well as the analysis of protein–ligand interactions. Reprinted from Int. J. Mass Spectrom., Vol. 420, Mikhailov, V. A.; Griffiths, R. L.; Cooper, H. J. Liquid extraction surface analysis for native mass spectrometry: Protein complexes and ligand binding, pp. 43—50 (ref 150). Copyright 2017, with permission from Elsevier.