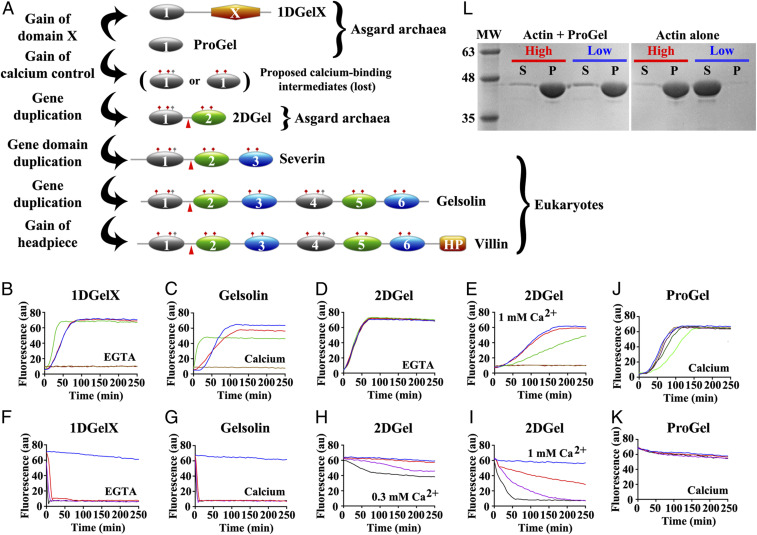
Fig. 1.
Thor gelsolins and actin regulation. (A) Schematic representation of the three Thor gelsolin architectures and the hypothetical evolution of the gelsolin family. Ovals depict gelsolin domains. Ticks indicate potential calcium-binding residues and red triangles denote a central WH2-like motif. Since Type II calcium-binding sites (48) (red ticks) are found in both domains of 2DGel, a calcium-binding single-domain protein likely existed in evolution that is not found in the current sequence databases. This is indicated by the “proposed calcium-binding intermediates.” The Type I site (48) (gray ticks) may have been present in this proposed calcium-binding intermediate, and later lost from domain two after the first gene duplication. Alternatively, the Type I site may have appeared in domain one after the first gene duplication. The architectures of typical eukaryotic gelsolin-like proteins are included for comparison. (B–E) Pyrene-actin polymerization profiles of 2 μM actin (blue) supplemented with (B) 1DGelX (1 mM EGTA), at 10 nM (red), 0.1 μM (green), or 2 μM (fawn) or 16 μM (dark brown), (C) supplemented with 5 nM (red), 0.05 μM (green), 2 μM (fawn) human gelsolin (0.3 mM CaCl2), or supplemented with (D) 2DGel (1 mM EGTA) or (E) 2DGel (1.0 mM CaCl2) at the concentrations in B. (F–I) Actin depolymerization profiles of 2 μM actin (blue), supplemented by (F) 1DGelX (1 mM EGTA), at 2 μM (red), 8 μM (lilac), or 32 μM (black), (G) human gelsolin in 0.3 mM CaCl2, concentrations as in C, (H) 2DGel (0.3 mM EGTA) or (I) 2DGel (1 mM CaCl2) at the concentrations in F. Two other 2DGel orthologs, 2DGel2 and 2DGel3, showed additional filament nucleation activity and more potent severing activity. All three 2DGel proteins were less active at 0.3 mM than at 1 mM Ca2+, and inactive in 1 mM EGTA in terms of severing activity (SI Appendix, Fig. S2 E–P). (J) Pyrene-actin polymerization profiles of 2 μM actin (blue) supplemented with 2 μM (fawn), 8 μM (lilac), 32 μM (dark green), or 128 μM (light green) ProGel in 0.3 mM Ca2+. (K) Pyrene-actin depolymerization profiles of 2 μM actin (blue) supplemented with 10 nM (red), 0.1 μM (green), 2 μM (beige), or 16 μM (dark brown) ProGel in 0.3 mM CaCl2. (L) SDS/PAGE analysis of actin filaments (8 μM) in the presence or absence of ProGel (256 μM). At 150,000 × g (high) filaments were pelleted in both conditions, whereas at 10,000 × g (low) actin was pelleted as bundles only in the presence of ProGel.