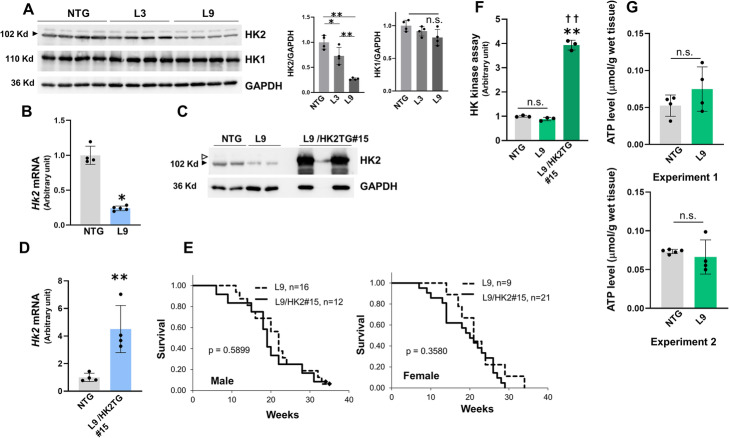
Fig. 3.
Analysis of HK2 expression, HK activity and ATP content of αMHC/miR-143/145TG (L9) mice and characterization of αMHC/miR-143/145/HK2TG (L9/HK2) mice. a Whole cell extracts from the hearts of 3-month old male L3 and L9 mice were examined using the indicated antibodies. The right panels show the relative densitometric analysis of the western blots. The results are presented as the means ± SD. Significance was assessed with one-way ANOVA followed by a post hoc Tukey test (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01). b Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of Hk2 mRNA in the hearts of 3-month old male L9 mice. The results are presented as the means ± SD with the unpaired t-test applied to determine significance (n = 4 ~ 5; *p < 0.05 vs. NTG). c Western analysis of HK2 in the hearts of 3-month old male L9 and L9/HK2 mice. Whole cell extracts were examined with an anti-HK2 antibody. The white and black arrowheads respectively indicate the transgenic human HK2 and the endogenous mouse HK2. d Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of Hk2 mRNA in the hearts of 3-month old male of L9/HK2 mice. Primers with common binding sites for human and mouse Hk2 genes were used. The results are presented as the means ± SD with the unpaired t-test applied to determine significance (n = 4; **p < 0.01 vs. NTG). e Kaplan-Meier survival analysis of L9 and L9/HK2 mice. Data were analyzed using log-rank test. f Hexokinase assay of the hearts of 3-month old male L9 and L9/HK2 mice. The results are presented as the means ± SD. Significance was assessed with one-way ANOVA followed by a post hoc Tukey test (n = 3; **p < 0.01 vs. NTG, ††p < 0.01 vs. L9). g ATP content assay in the hearts of 4-week old male L9 mice. The results are presented as the means ± SD with the unpaired t-test applied to determine significance (n = 4 ~ 5). Experiments 1 and 2 were performed independently. a–d, f Similar results were obtained in at least two independent experiments