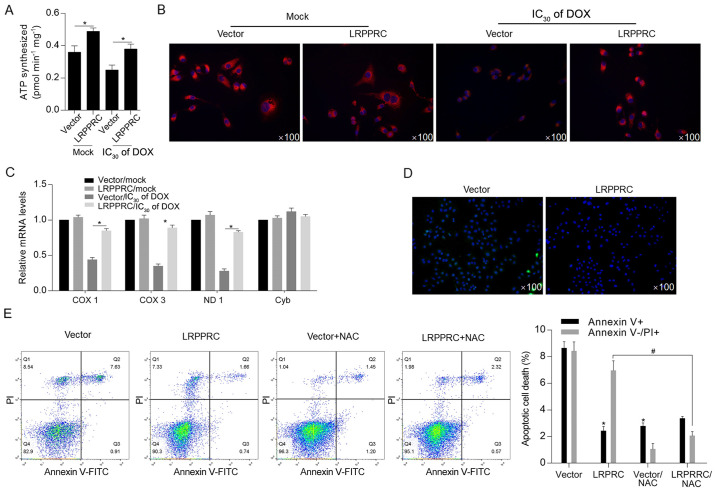
Figure 3.
DOX-induced LRPPRC exerts protective effects against DOX exposure potentially via scavenging ROS. (A) Following DOX exposure, the effect of LRPPRC overexpression on ATP synthesis was examined. (B) Mitochondrial mass was measured using MitoTracker Red staining. (C) To evaluate the effect of LRPPRC on mitochondrial transcriptional activity, the expression levels of COX 1, COX 3, ND1 and Cyb were detected via reverse transcription-quantitative PCR. (D) ROS accumulation was detected following DOX exposure at IC30 for 24 h. (E) Annexin V-FITC/PI double staining followed by flow cytometric analysis was performed to detect apoptotic and non-apoptotic cell death. *P<0.05 vs. vector group; #P<0.05 vs. LRPPRC group. LRPPRC, leucine-rich pentatricopeptide repeat-containing; DOX, doxorubicin; PI, propidium iodide; COX, cytochrome c oxidase subunit; ND1, NADH dehydrogenase subunit 1; Cyb, cytochrome b; NAC, N-acetyl-L-cysteine; ROS, reactive oxygen species.