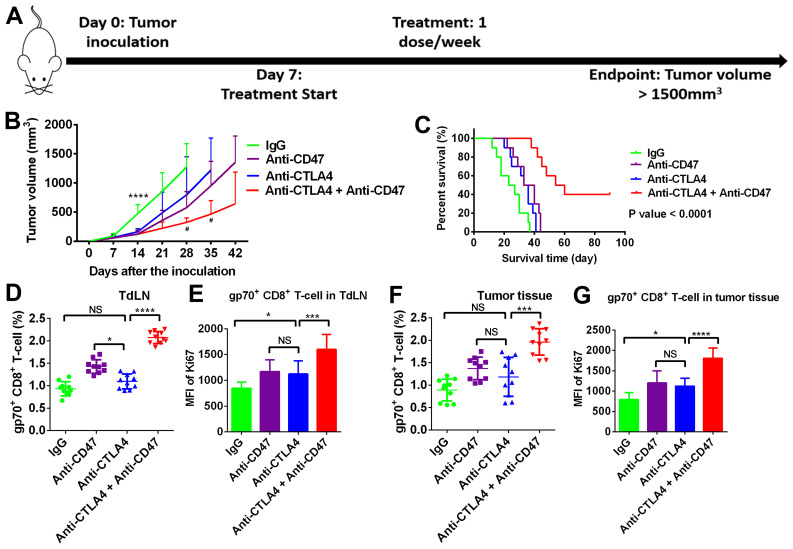
Figure 5.
Anti-CD47 treatment enhanced the efficacy of anti-CTLA4 treatment via stimulating anti-tumor immunity. (A) The experimental scheme. (B) Growth of tumors co-treated with anti-CD47 and anti-CTLA4 antibodies was slower in comparison with tumors treated with monotherapy. ****P<0.0001 vs. IgG group; #P<0.05 vs. anti-CTLA4 group) (C) Mice co-treated with anti-CD47 and anti-CTLA4 antibodies exhibited longer survival as compared with mice receiving monotherapy. (D) Number of gp70+ CD8 T-cells and (E) Ki-67 expression in the tumor-draining lymph node were increased by anti-CD47 and anti-CTLA4 combination treatment. (F) Number of gp70+ CD8 T-cells and (G) Ki-67 expression levels in tumor tissues were higher in the anti-CD47 and anti-CTLA4 combination treatment group. Sample size=10 per group. *P<0.01, ***P<0.001 and ****P<0.0001. CTLA4, cytotoxic T-lymphocyte associated protein 4. CD47, cluster of differentiation 47; MFI, mean fluorescence intensity.