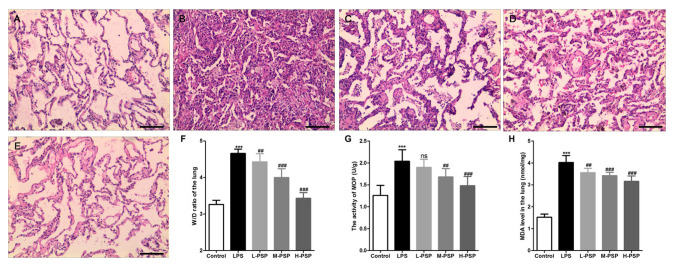
Figure 1.
Effect of PSPs on LPS-induced pathological changes in the lungs in ALI rats. (A-E) Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining was used to observe pathological changes in the lungs of (A) control group, (B) LPS group, (C) L-PSP group, (D) M-PSP group and (E) H-PSP group of rats. (F) The value of the W/D in lung tissues of the different groups. (G) MOP activity in lung tissues of the different groups. (H) The MDA level in lung tissues of the different groups. A total of 10 rats in each group, each indicator for each rat was tested at least 3 times independently; ***P<0.001 vs. the control group; NS, not significant at P>0.05; ##P<0.01 and ###P<0.001 vs. the LPS group. Scale bar, 100 µm. PSPs, Polygonatum sibiricum polysaccharides; ALI, acute lung injury; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; MOP, myeloperoxidase; MDA, malondialdehyde; W/D, wet/dry weight ratio. Groups: L-PSP, 20 mg/kg; M-PSP, 40 mg/kg; H-PSP, 80 mg/kg PSPs.