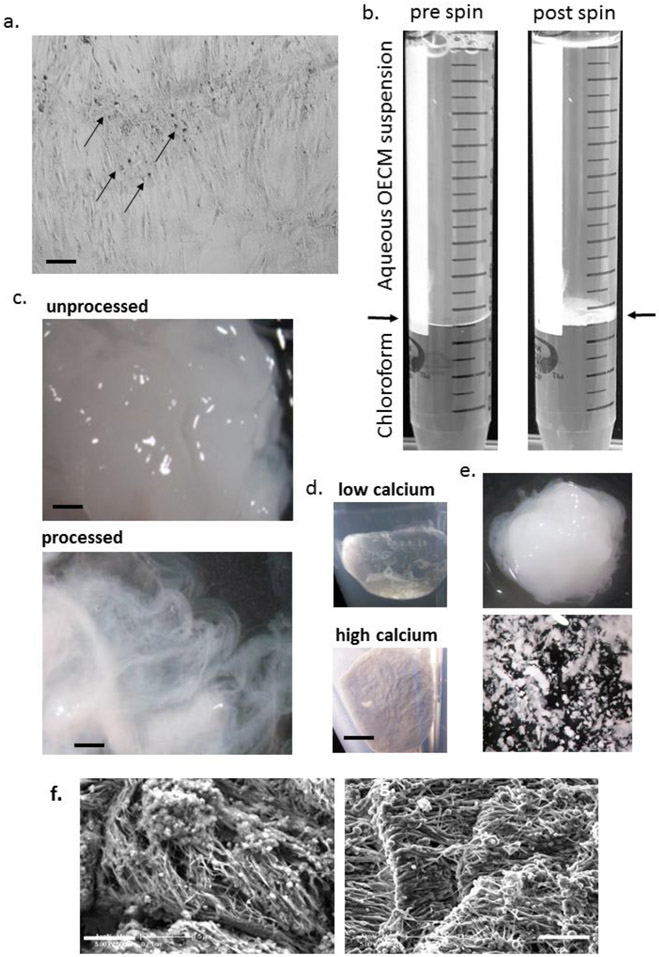
Figure 2: Purification and morphology of OECM:
Panel a: phase-contrast micrograph of osteogenic culture with dense nodules of OECM (arrowed). Panel b: processing of OECM with chloroform before and after centrifugation. The disk of OECM is present at the interface (arrowed) after spinning. Panel c: Appearance of cell/OECM mixture before processing (above) and OECM after processing (below) dispersed in water illustrating fibrous appearance (adapted with permission from ref. 18). Panel d: Appearance of acetone-dried pellets generated under conditions that deposit low calcium (above) or high calcium (below). Panel e: Low calcium OECM (above) generates a putty-like matrix upon partial drying, OECM with high calcium content fragment upon manipulation (below). Panel f: Scanning electron microscopy of OECM before (left) and after (right) processing. For panel a: bar = 200 μm. For panel c: bar = 500 μm. For panel d, e: bar = 2 mm. For panel f: bar = 5μm.