Table 1.
Chemical properties and PDE4 inhibitory potencies of four compounds (3–6) selected for radiolabeling from the indicated desmethyl precursors (7–10).
| Inhibitor | Structure | cLogPa | cLogD7.4a | PET MPO | IC50 (nM)b | Selectivity for PDE4D* over PDE4B | SUVc | Labeling precursor | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDE4D7* | PDE4B | ||||||||
| 3 (T1953) | 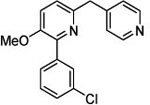 |
2.67 | 2.66 (3.45) | 3.1 | 5.12 | 720 | 141 | 0.94 | 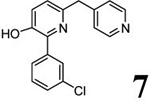 |
| 4 (T2525) | 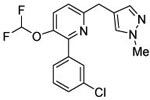 |
3.58 | 3.58 (3.07) | 2.6 | 0.5 | 858 | 1672 | 1.44 | 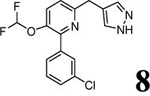 |
| 5 (T1660) | 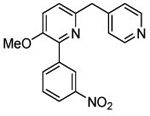 |
3.94 | 3.93 (3.38) | 3.5 | 2.8 | 280 | 101 | 1.76 | 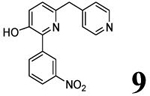 |
| 6 (T1650) | 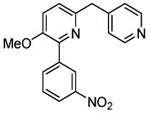 |
3.48 | 3.48 (2.89) | 3.9 | 3.5 | 1120 | 320 | 1.76 | 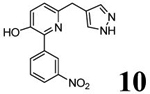 |
LogP and logD7.4 values were calculated with Pallas software; values in parentheses were measured with the radiolabeled compound (see SI for details).
Human PDE4D7* contained a mutation of S129D to mimic activation by cAMP-dependent protein kinase A (PKA), whereas PDE4B1 contained the mutation S133D.
Brain uptake in mice after intravenous dosing (SUV = standardized uptake value calculated as ([brain Cmax (ng/mL)/dose (mg/kg)/1000]).
