Figure 4. Characterizing resistance to GSK923295 in KBM7 cells.
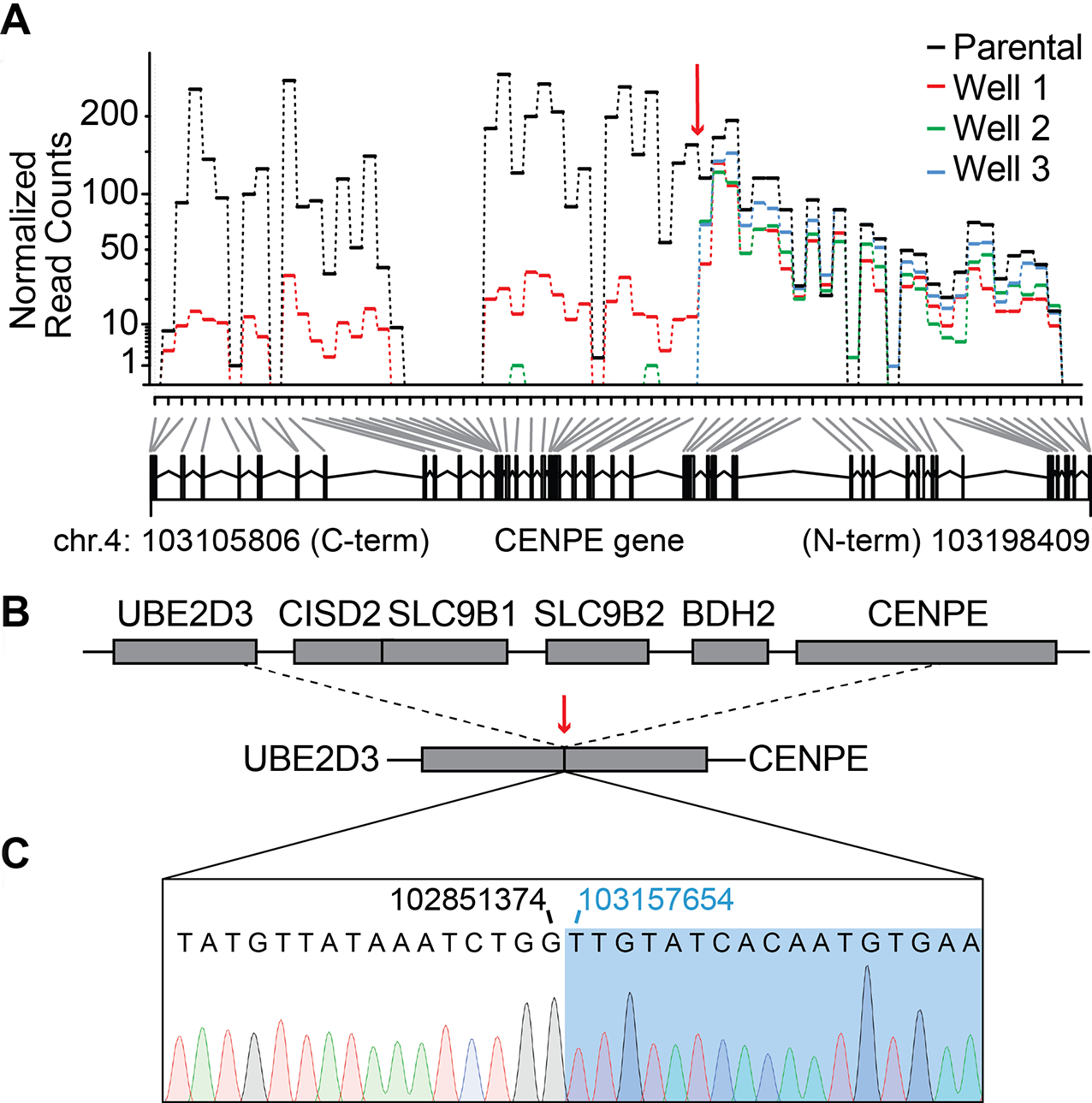
(A) Exon usage over CENPE gene in parental and GSK923295-resistant KBM7 cells. Normalized read counts for each sample are shown (top panel). Deletion site in the CENPE gene is indicated (red arrow). Counting bins generated by the DexSeq algorithm are also shown (bottom panel, gray and black lines). First and last base pairs of the CENPE gene on chromosome 4 are indicated.
(B) Schematics show UBE2D3-CENPE genomic locus in wild-type (top) and GSK923295-resistant KBM7 cells (bottom). Deletion/fusion site is indicated (dashed lines and red arrow).
(C) Sanger sequencing trace of the deletion/fusion site in GSK923295-resistant KBM7 cells. Positions of the last base pair of the UBE2D3 gene (black) and the first base pair of the CENPE gene (blue) at the deletion/fusion site are indicated.
