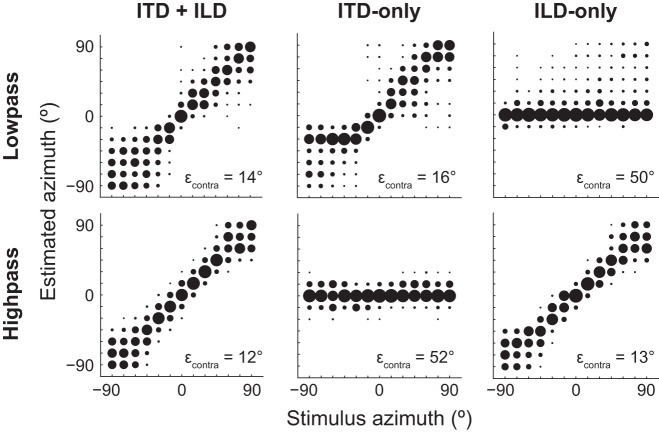
Fig. 9.
Maximum-likelihood estimate of stimulus azimuth from the neural population response is consistent with duplex theory. In each panel the maximum-likelihood decoder was trained on population responses from the interaural time difference (ITD)+interaural level difference (ILD) condition to low-pass (top) and high-pass (bottom) noise at 70 dB SPL (n = 42 neurons). The decoder was tested on population responses to either low- or high-pass noise in the ITD+ILD (left), ITD-only (center), and ILD-only (right) conditions. Bubble diameter indicates fraction of estimated azimuths over 1,000 trials of each stimulus azimuth. Root mean square (RMS) localization error (εcontra) over all contralateral azimuths (0° to 90°) indicated at bottom right of each plot. The decoder accurately estimated contralateral azimuths of low- and high-pass noise under ITD-only and ILD-only cue conditions, respectively.