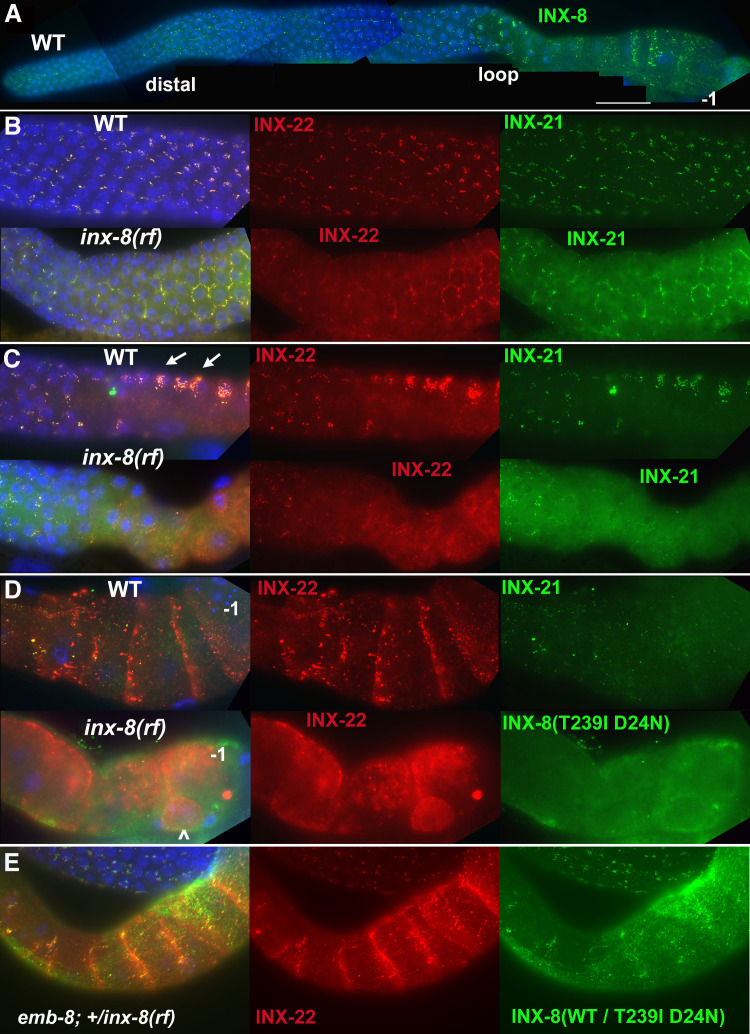
Figure 2. INX-8(T239I D24N) compromises gap junction formation between soma and germline.
(A) Somatic INX-8 in wild-type (WT) gonads localizes to puncta representing soma-germline gap junctions where DTC or sheath cells overlie germ cells. (B) In WT distal gonad arms, gap junction puncta aggregate in small clusters associated with each germ cell; in inx-8(rf) distal arms, gap junction puncta localize more apically, where sheath dips down between germ cells, outlining the cell (honeycomb pattern). Localization of INX-21 and INX-22 define the two different classes of germline gap junction hemichannels, both of which include INX-14 subunits. (C) At the loop region, WT gap junction puncta form large aggregates (arrows) which are absent in inx-8(rf). (D) In WT proximal arms, gap junction formation with INX-22-containing hemichannels is extensive; in inx-8(rf), INX-22 and INX-8(T239I D24N) are strongly expressed but show little evidence of gap junction formation. ‘–1’ indicates the most proximal oocyte; inx-8(rf) hermaphrodites frequently show undersized oocytes at this position as well (<). (E) Heterozygous +/inx-8(rf) shows little effect on gap junction localization in an emb-8(hc69ts) background at 22°C. Antibodies specific to INX-8, INX-21, or INX-22 were used as indicated. DAPI-stained DNA in blue. Bar, 50 μm.