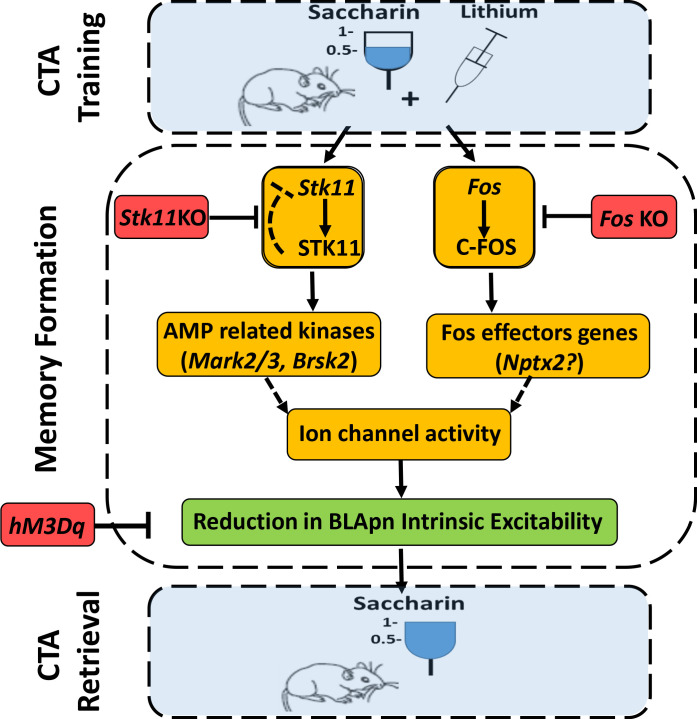
Figure 9. An integrated model for the formation of CTA memory.
CTA training mice associate consumption of palatable saccharin with gastric malaise (induced by systemic injection of lithium chloride). Memory formation: CTA training increases the activity STK11 and C-FOS in BLA projection neurons (BLApn) via initially separate signaling pathways. CTA increases STK11 protein but reduces its mRNA, possibly through feedback control. STK11 activation results in downstream phosphorylation and activation of AMP related kinases, likely including Mark2/3, Brsk2, and Sik3, which are abundant in BLApn. C-FOS, an activity dependent transcription factor, induces the transcription of effector genes such as Nptx2 which increases following CTA training and is known to bind not only ligand-gated receptors, but also voltage-gated ion channels. The two pathways reduce BLApn intrinsic excitability through unknown mechanism(s). CTA retrieval: Reduced BLApn intrinsic excitability plays a key role in CTA memory formation, reducing saccharin consumption in test trials. Blue-behavioral level, Orange-molecular level, Green-cellular level, Red-conditions impairing memory. Dashed line arrows are hypothesized connections.