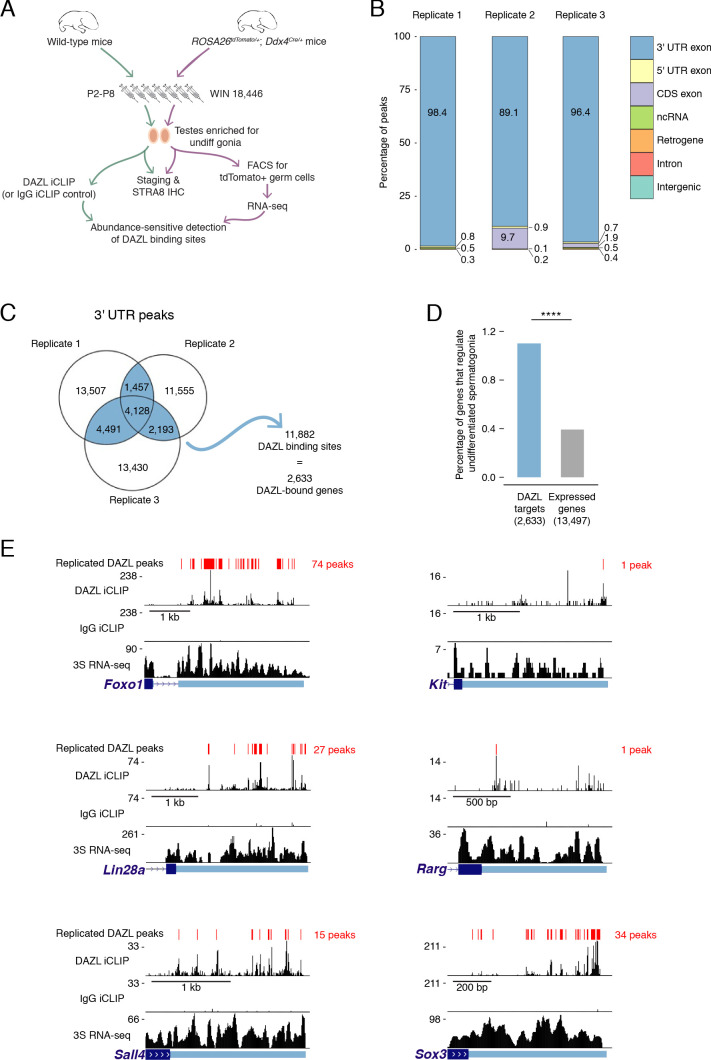
Figure 2. Identification of DAZL-bound transcripts in undifferentiated spermatogonia via iCLIP reveals DAZL’s regulation of spermatogonial factors.
(A) Schematic of the synchronization of spermatogenesis to obtain undifferentiated spermatogonia via the 2S method for iCLIP (green arrows) and via the 3S method for RNA-seq (purple arrows). WIN 18,446 was used to synchronize spermatogenesis by blocking spermatogonial differentiation, and samples were histologically staged to verify successful synchronization. For 3S samples, germ cells were sorted from synchronized testes. (B) Genomic distribution of DAZL iCLIP peaks identified in three biological replicates (TPM ≥1; FDR < 0.05). (C) Venn diagram showing overlap of DAZL iCLIP peaks in expressed 3' UTRs (TPM ≥1) among three biological replicates. Replicated peaks (i.e., present in at least two of three replicates) were identified. After merging replicated peaks that fell on consecutive nucleotides, 11,882 DAZL binding sites (present in at least two of three replicates; highlighted in blue) were identified. These binding sites correspond to 2,633 genes, which are designated as the DAZL-bound genes. (D) Enrichment of factors that regulate the development and differentiation of undifferentiated spermatogonia in DAZL targets compared with all genes expressed in undifferentiated spermatogonia (one-tailed hypergeometric test). Number of genes (n) in each group designated in parentheses in labels along x-axis.****, p<0.0001. (E) DAZL iCLIP, IgG iCLIP, and 3S RNA-seq gene tracks showing exemplary DAZL-bound genes that are required for spermatogonial proliferation and expansion (Lin28a and Sox3) or differentiation (Kit, Foxo1, Rarg, and Sall4). Each iCLIP track represents the crosslinked sites from the sum of unique reads from three biological replicates. The RNA-seq track represents the sum of two biological replicates. The scale of each gene track is marked on the left. 3' UTRs are in light blue.