FIGURE 2.
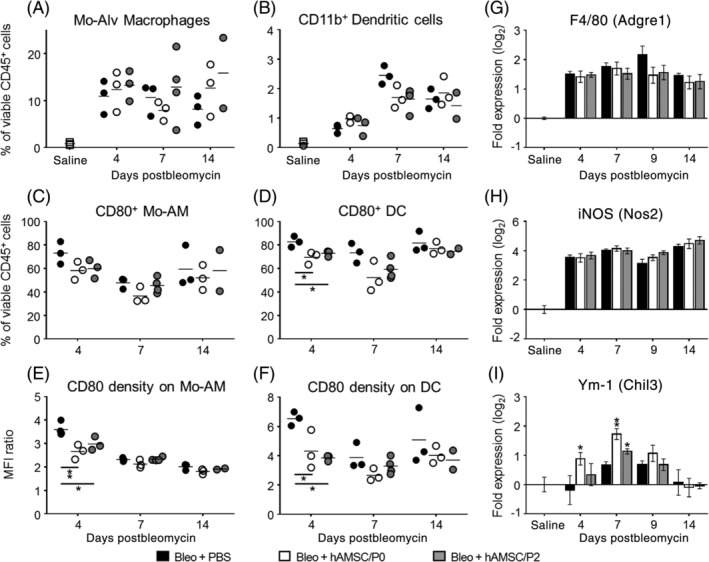
Human amniotic mesenchymal stromal cells (hAMSCs) alter antigen presenting cells in bleomycin‐induced inflammation. Bleomycin challenge increased alveolar levels of both monocyte‐derived alveolar macrophages (Mo‐Av Macrophages, Mo‐AM) (A, Bleo+PBS group) and CD11b+ dendritic cells (DC) (B, Bleo+PBS group). hAMSC treatment did not affect levels of Mo‐AM and DC (A,B), however it reduced the levels of Mo‐AM and DC expressing the costimulatory molecule CD80 (C,D) and more strongly reduced the density with which CD80 was expressed on the surface of these cells (E,F). With regard to macrophage subsets, bleomycin challenge increased lung mRNA expression of F4/80 (a pan marker of macrophages; G, Bleo+PBS group) and of iNOS (a marker of M1 macrophages; H, Bleo+PBS group) while did not change expression of Ym‐1 (a marker of M2 macrophages, I). hAMSC treatment did not affect expressions of F4/80 and iNOS, in contrast it increased the expression of Ym‐1 (I), suggesting a polarization toward M2 anti‐inflammatory phenotype. Alveolar levels of Mo‐AM and DC were analyzed by flow cytometry, as percentage of viable CD45 positive cells in bronchoalveolar lavage collected from bleomycin‐challenged mice treated with amniotic cells (Bleo+hAMSC/P0 and Bleo+hAMSC/P2) or not (Bleo+PBS). Density of CD80 expression was evaluated as median fluorescence intensity ratio between positive and negative cells. Data from mRNA levels analysis are expressed as log2 of the fold change from the saline‐instilled group. These data are reported as mean ± SE of n = 4 (day 4) and n = 5‐7 (days 7, 9, and 14) samples. *P < .05, **P < .01 compared to control (Bleo+PBS) group
