Fig. 2.
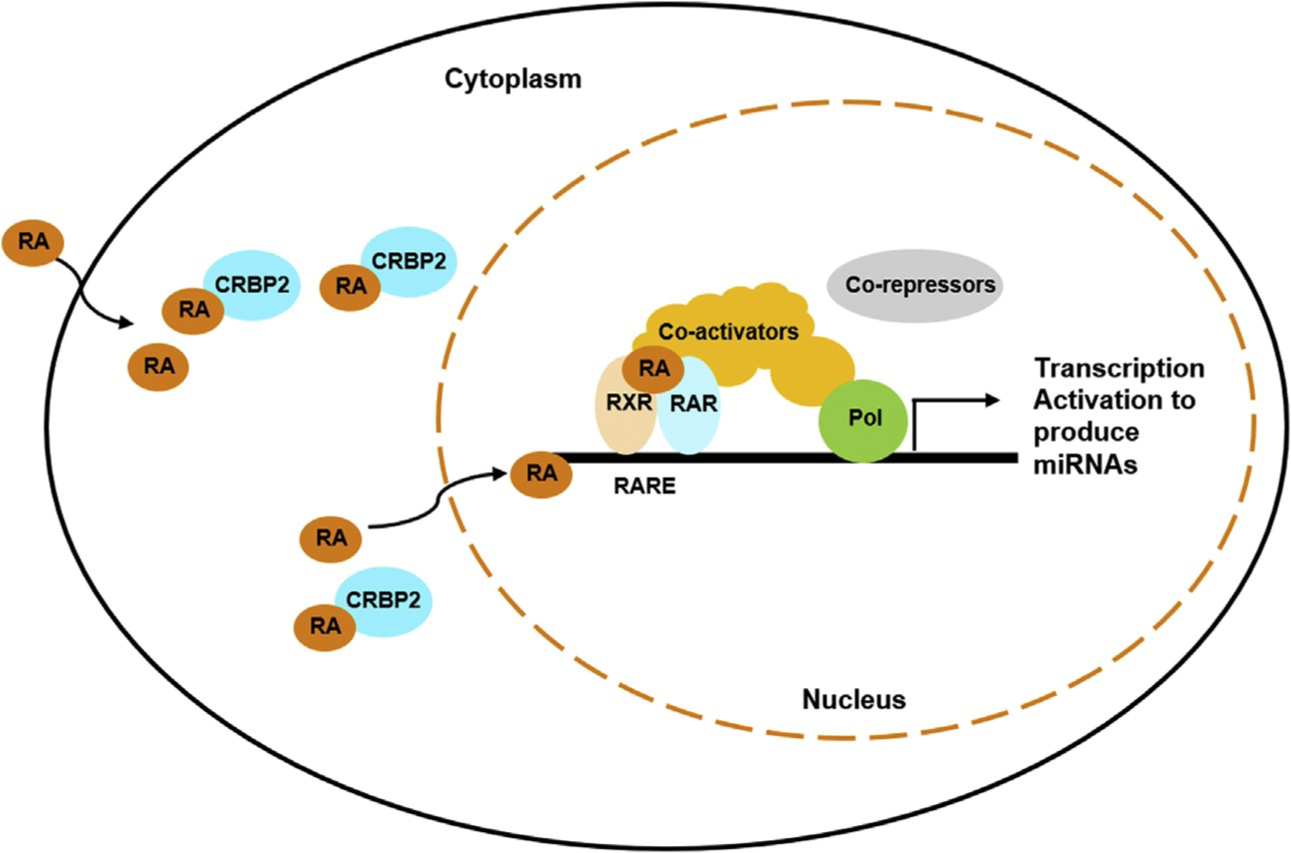
Retinoic acid and its receptor-mediated gene expression. RA is transported into the cell and bind to CRABP2 (cellular RA binding protein). In the nucleus, RA binds to nuclear receptors RXR and RAR heterodimer, which recognizes the RA receptor responsive element (RARE) located on the target gene, to regulate gene expression. The transcriptional activation requires the recruitment of coactivators and the departure of co-suppressors. Once miRNA is produced, it can silence the RA receptors, the transcriptional co-regulators, or other specific targets to modulate the effects of RA.
