Fig. 3. 2-way- and 4-way- repeat configurations are required for efficient replication of X and Y2 RNA.
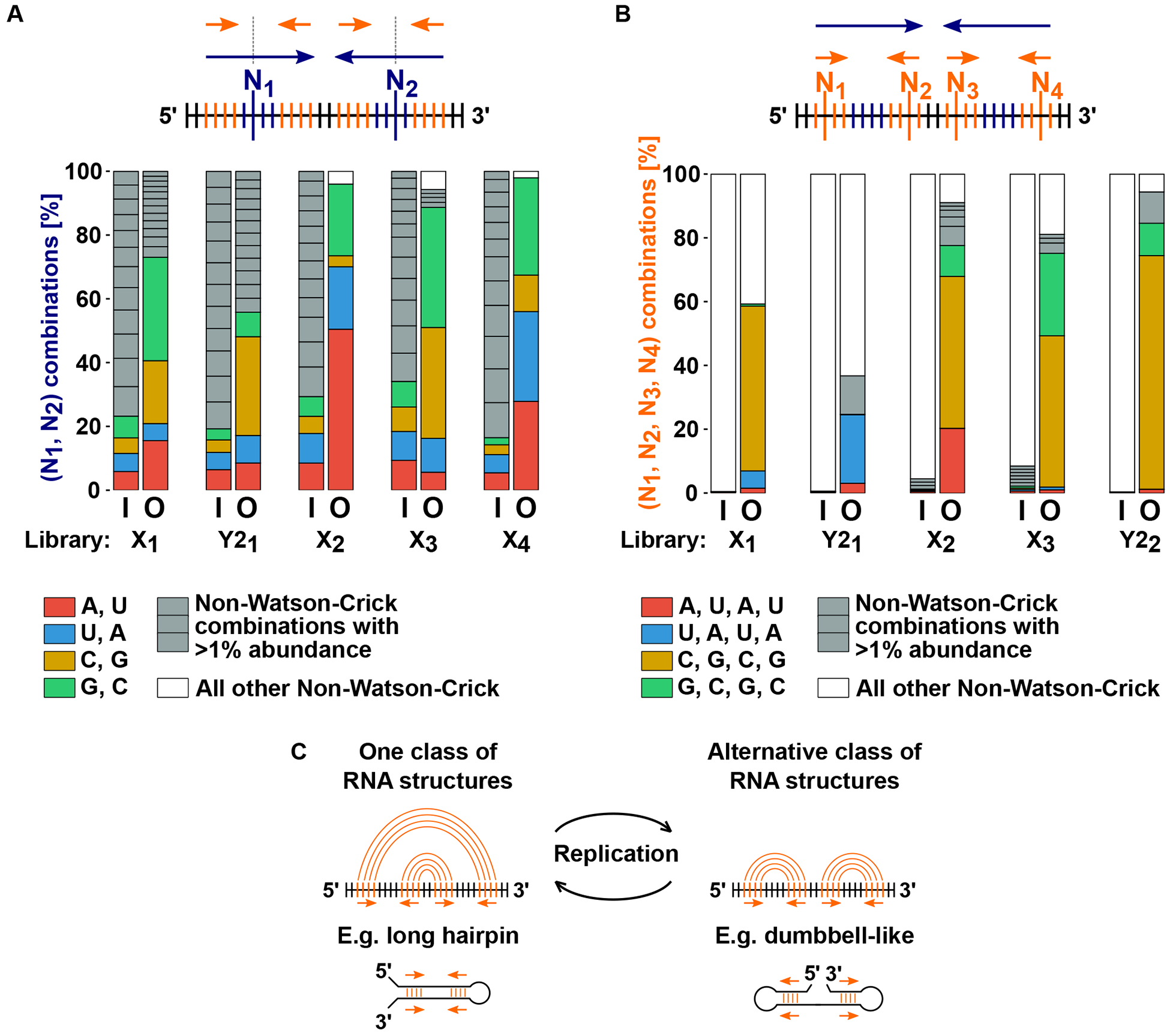
Six degenerate libraries (X1-X4, Y21-Y22) were constructed by randomizing the base identities at a subset of sequence positions in either X RNA or Y2 RNA. Degenerate libraries were used as templates in T7 RNAP reactions, and RNA populations before replication [input “I” on x axes of bar graphs in panels (A) and (B)] and after replication [output “O” on x axes] were sequenced to test whether Watson-Crick base combinations were enriched at randomized positions after replication. (A) 2-way repeat requirement was tested by randomizing bases at two potentially base pairing positions (“N1” and “N2”) in parts of the 2-way repeat (blue arrows) that are non-overlapping with the 4-way repeat (orange arrows). (B) 4-way repeat requirement was tested by randomizing bases at four potentially base pairing positions (“N1” through “N4”) in the 4-way repeat. Color coding of bar graphs in panels (A) and (B): different Watson-Crick base combinations are shown in unique colors; abundant (>1%) non-Watson-Crick base combinations are shown individually in gray; infrequent (<1%) non-Watson-Crick base combinations are summed together and shown in white. (C) Shape-shifting model. 2-way repeat requirement provides evidence for a long hairpin RNA secondary structure whereas 4-way repeat requirement suggests the formation of an alternative RNA secondary structure during replication.
