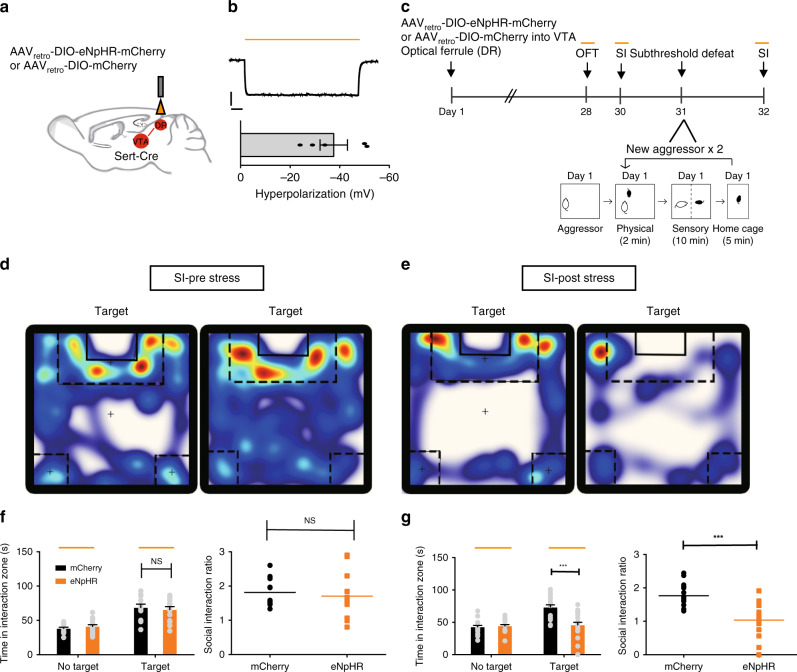
Fig. 5. Silencing of 5-HTDR→VTA neurons promotes stress susceptibility.
a Experimental setup for the expression of AAVretro-DIO-eNpHR-mCherry or control virus (mCherry) in 5-HTDR→VTA neurons and ferrule implantation into the DR. b Whole-cell current-clamp recordings of eNpHR-mCherry neurons in response to 593 nm light (yellow lines) in DR slices showed that yellow light drove hyperpolarization (top). Summary plot (bottom) showing robust light-evoked hyperpolarization (n = 5 neurons from two mice). Scale, 20 mV, 1 s. c Experimental timeline of the inhibition of 5-HTDR→VTA neurons (top panel) and a schematic of the subthreshold paradigm (bottom panel). d, e Representative traces of animals expressing eNpHR in 5-HTDR→VTA neurons during the social interaction test with light stimulation (d) or after subthreshold defeat stress with optical stimulation (e). Warmer colors indicate more time spent. f No significant difference was observed in social interaction time (eNpHR, n = 13 mice; mCherry, n = 11 mice; one-way ANOVA, F1,22 = 0.177, P = 0.678) or social interaction ratio during inhibition of 5-HTDR→VTA neurons (eNpHR, n = 13 mice; mCherry, n = 11 mice; one-way ANOVA, F1,22 = 0.220, P = 0.644). g Silencing of 5-HTDR-VTA neurons following subthreshold defeat stress exposure elicits social aversion; (eNpHR, n = 18 mice; mCherry, n = 17 mice; one-way ANOVA, interaction: F1,33 = 18.287, P < 0.001, SI ratio: F1,33 = 28.155, P < 0.001). Data are represented as mean ± SEM. NS: not statistically significant; **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.