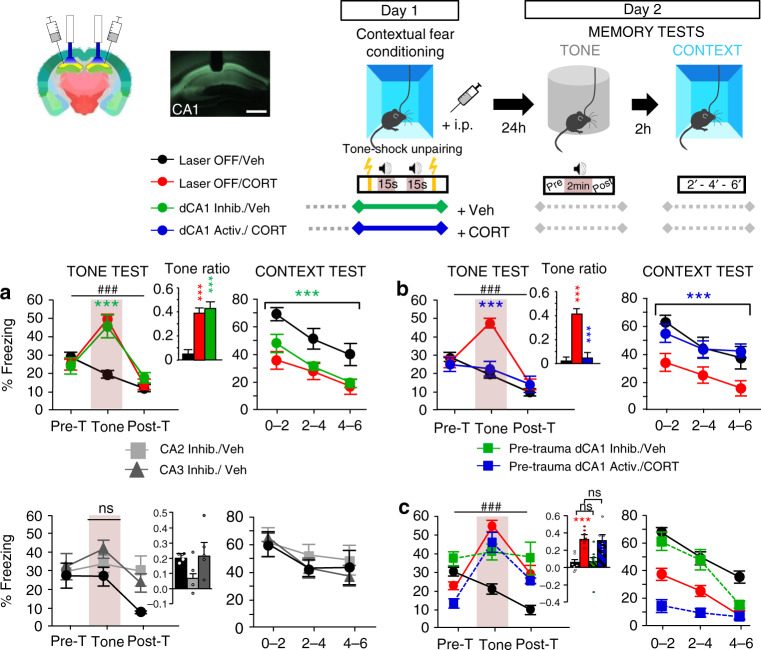
Fig. 1. dCA1 inhibition during stress produces PTSD-like memory whereas dCA1 activation in traumatic conditions prevents PTSD-like memory.
Top panel, scheme illustrating the optogenetic approach (Image credit: Allen Institute), contextual fear conditioning (Day 1) and memory tests (Day 2): re-exposure to the tone alone in a familiar chamber, and then to the conditioning context 2 h later. Scale bar: 500 µm (a) top, compared to normal contextual fear memory attested by no fear response to the tone (no increase of freezing to the tone, left panel) and high fear response to the context (right panel) in (Laser OFF, n = 15) Vehicle-injected mice, PTSD-like memory in (Laser OFF, n = 13) CORT-injected mice is attested by a fear response specific to the tone (repeated measures (RM) of freezing during the tone test: F2,24 = 35.908; P < 0.0001; tone ratio vs 0; P < 0.0001) associated with decreased fear to the context. A similar difference between the groups is observed when NaCl is replaced by HBC as vehicle [data not shown]. dCA1 inhibition during conditioning produces PTSD-like memory in Veh-injected mice (n = 13; RM × laser condition: F4,76 = 20.184; P < 0.0001). Although all groups display relatively high pre-tone freezing levels in the familiar chamber, these levels are lower than those expressed in the conditioning chamber (left vs. right: all F > 6.29, all P < 0.028). a, bottom, dCA2 or dCA3 inhibition does not produce PTSD-like memory (n = 4–5; laser condition: F2,11 = 1.755; P = 0.2181). b Compared to control (Laser OFF; n = 11) CORT-injected (PTSD-like) mice, CORT-injected mice submitted to dCA1 activation (n = 11) during conditioning display a normalized (contextual) fear memory (RM × laser condition: F2,40 = 15.684; P < 0.0001). c Pre-conditioning (5 min before) dCA1 inhibition or activation does not change the nature of the fear memory formed: normal (contextual) or PTSD-like fear memory in Veh- and CORT-injected mice, respectively (n = 7–8). Data are presented as mean ± SEM. This experiment was repeated independently once with similar results. See table in the “Methods” section for detailed sample sizes. Statistical significance was assessed by RM (three blocks) two-sided ANOVA with post hoc test when appropriate. ***P < 0.005. ###: block × condition interaction (P < 0.005). Source data are provided as a Source Data file.