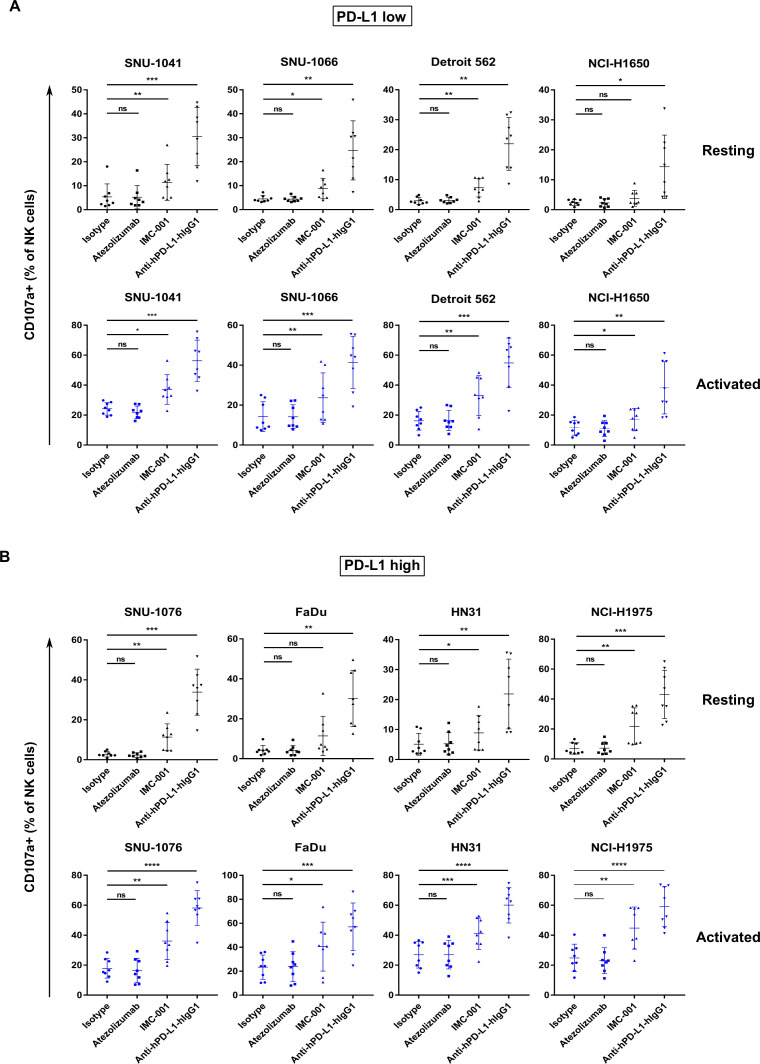
Figure 3.
Enhanced cytotoxicity of NK cells against human cancer cells through anti-PD-L1 mAb-mediated ADCC. Cytotoxicity of primary NK cells mediated by anti-PD-L1 mAb ADCC was measured in human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma and non-small-cell lung cancer cell lines using a CD107a degranulation assay. PBMCs from healthy donors were used for effector cells both in resting (black) and activated (blue) states (n=8). PBMCs were cultured overnight or activated with 1 ng/mL interleukin-15 for 3 days. Cancer cell lines were pretreated with anti-PD-L1 mAbs for 30 min. After washing, human cancer cell lines were cocultured with effector cells 1 hour at ratio of 1:1. (A) Results of CD107a degranulation assay in PD-L1 low-expressing and (B) PD-L1 high-expressing cancer cell lines. Statistical significance across groups was determined by one-way analysis of variance. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001. ADCC, antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity; mAb, monoclonal antibody; NK, natural killer; ns, not significant; ns, not significant; PBMC, peripheral blood mononuclear cell; PD-L1; programmed death-ligand 1.