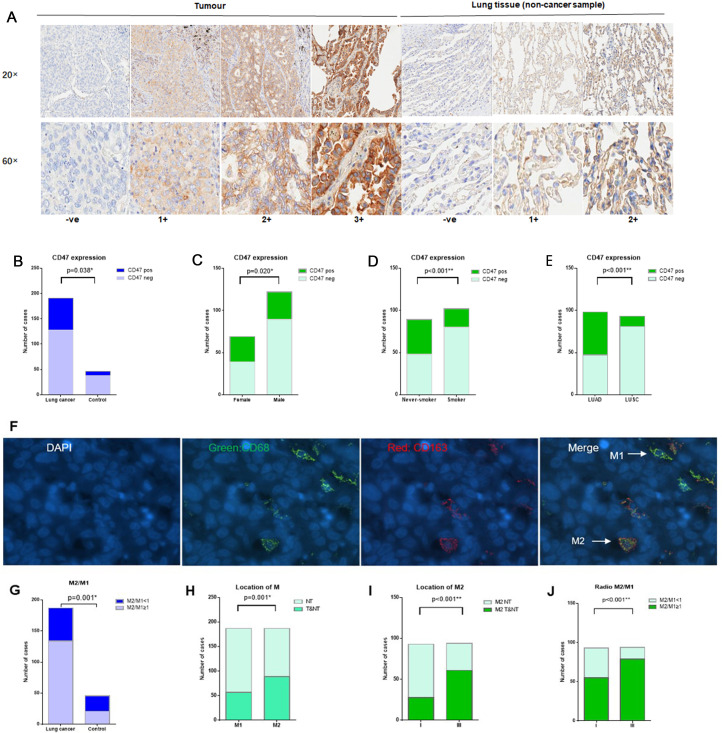
Figure 1.
CD47 expression and tumour-associated macrophage infiltration. (A) Representative IHC images of different CD47 expression level scores in tumour and lung tissue (control respiratory disease sample). (B) CD47pos expression in NSCLC is higher than in the control group (infection lung tissues) (33.0% vs 17.4%, p=0.038). (C) Tumour CD47pos expression in female patients with NSCLC was higher than in male patients with NSCLC (43.5% vs 27.0%, p=0.020). (D) Tumour CD47pos expression in never-smokers with NSCLC was higher than in smokers with NSCLC (46.1% vs 21.6%, p<0.001). (E) Tumour CD47pos expression in LUAD was higher than in LUSC (52.0% vs 12.9%, p<0.001). (F) Representative immunofluorescence images of CD68pos macrophages, CD163pos macrophages, M2-TAMs (CD8pos, CD163pos) and M1-TAMs (CD68pos, CD163neg). (G) High M2/M1 ratios were more frequently observed in NSCLC compared with the control group (71.7% vs 45.7%, p=0.001). (H) M2 infiltration in the tumour area was higher than M1 infiltration in the tumour area (89 vs 57, p=0.001). (I) M2 infiltration in the tumour area in stage III NSCLC was higher than in stage I NSCLC (64.2% vs 29.2%, p<0.001). (J) High M2/M1 ratios were more frequently observed in stage III NSCLC than in stage I NSCLC (83.1% vs 57.3%, p<0.001). *p<0.05, **p<0.001. CD47pos, cases with CD47 IHC scores of 2+ or 3+ were considered positive for tumour CD47 positive expression; CD47neg, cases with CD47 IHC scores of 1+ or ve (0) were considered negative for tumour CD47 expression; if, immunofluorescence; IHC, immunohistochemistry; LUAD, lung adenocarcinoma; LUSC, lung squamous cell carcinoma; NSCLC, non-small cell lung cancer; NT, non-tumour area; TAMs, tumour-associated macrophages; T&NT, tumour area and non-tumour area.