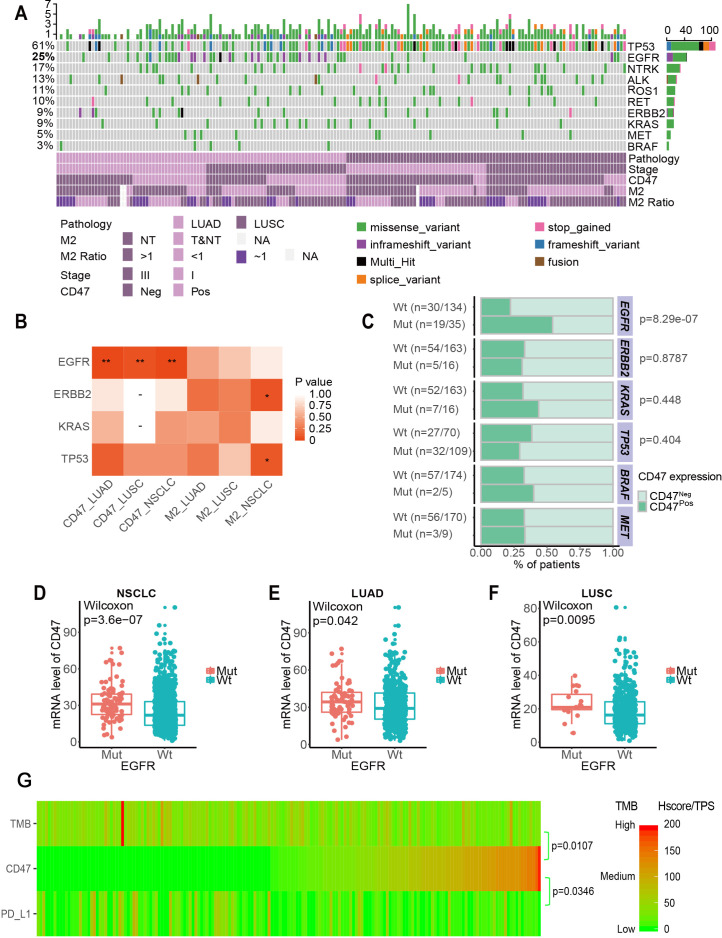
Figure 2.
Correlation between CD47 expression and driver gene mutations in NSCLC. (A) Landscape of the top 10 genes involved in NSCLC (ALK, BRAF, EGFR, ERBB2, KRAS, MET, NTRK, RET, ROS1 and TP53) among 179 patients and associated clinical information. (B) Correlation between immune infiltrate expression and genomic alterations in NSCLC. Only contingency tables with n>5 were included in the test. *p<0.1, **p<0.05. (C) Correlation between CD47 expression and four well-known mutant genes in NSCLC. (D to F) The correlation between CD47 mRNA and EGFR mutation in NSCLC (D), LUAD (E) and LUSC (F) in the Cancer Genome Atlas. P values were calculated using the Wilcoxon rank-sum test. (G) CD47 expression heatmap (H-score), PD-L1 (TPS) and TMB in NSCLC. CD47pos, CD47 positive; CD47neg, CD47 negative; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; LUAD, lung adenocarcinoma; LUSC, lung squamous cell carcinoma; mRNA, messenger RNA; mut, mutation; NSCLC, non-small cell lung cancer; NT, non-tumour area; T&NT, tumour area and non-tumour area; TMB, tumour mutation burden; TPS, tumour proportion score; Wt, wild-type.