FIGURE 1.
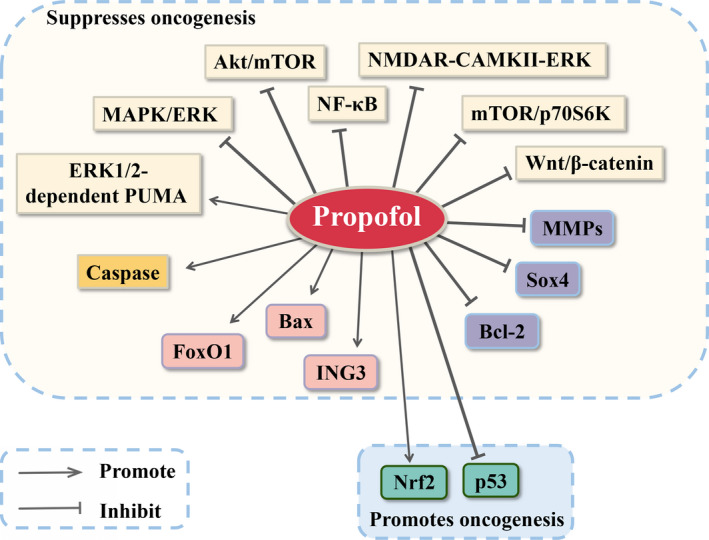
Propofol exerts tumour‐suppressive or oncogenic effects by regulation of related signalling pathways or downstream molecules in cancer cells. Akt, protein kinase B; Bax, B‐cell lymphoma‐2 associated X; Bcl‐2, B‐cell lymphoma‐2; CAMKII, calcium/calmodulin‐dependent protein kinase II; ERK, extracellular signal‐regulated kinases; FoxO1, Forkhead Box O1; ING3, inhibitor of growth 3; MAPK, mitogen‐activated protein kinase; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; NF‐κB, nuclear factor‐kappa B; NMDAR, N‐methyl‐D‐aspartate receptor; Nrf2, nuclear factor E2‐related factor‐2; p53, tumour protein P53; p70S6K, p70 ribosomal protein S6 kinase; Sox4, SRY‐box transcription factor 4; Wnt, wingless and proto‐oncogene integration‐1. “Arrows from propofol to → targets” means “activating targets.” “Blockade from propofol to targets” means “inhibiting targets”
