Figure 9. The proposed mechanism of HDAC8-mediated renal fibrosis.
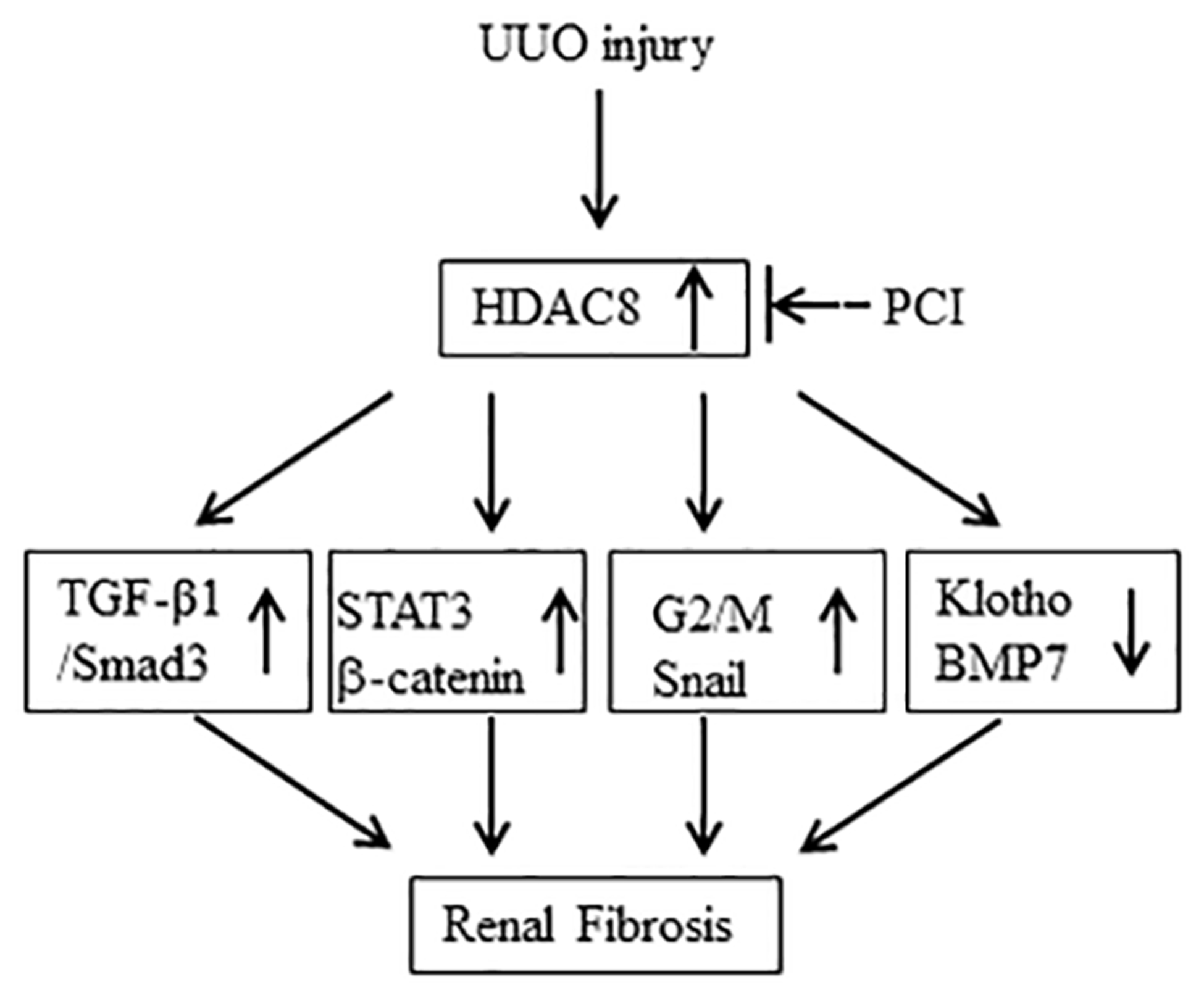
Injury to the kidney results in increased expression of HDAC8 in renal tubular cells. Increased HDAC8 activity leads to the activation of TGFβ/Smad3, STAT3, β-catenin signaling, induction of epithelial cells arrested at G2/M phase of cell cycle, upregulation of Snail and downregulation of klotho and BMP-7. Blocking class HDAC8 inhibits all these profibrotic responses.
