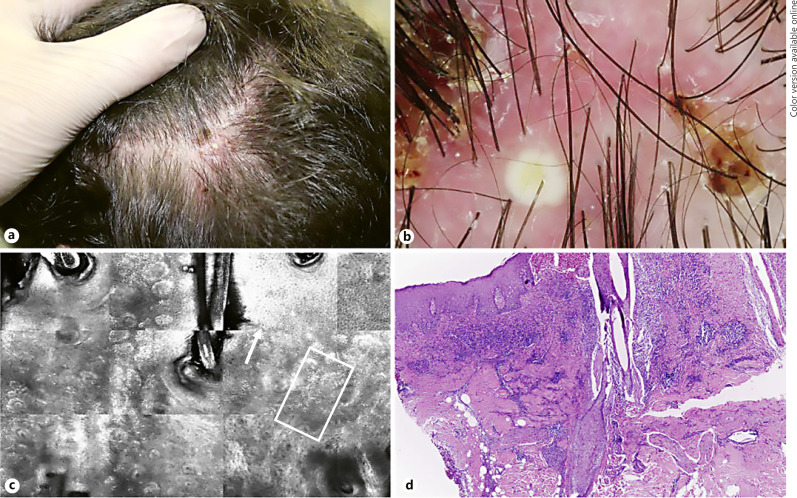
Fig. 2.
Clinical, dermatoscopic, confocal and histopathological features of FD. a Clinical image of an active lesion localized on temporo-parietal area, showing dermatoscopy follicular pustules, yellow tubular scaling and perifollicular haemorrhages (b). c RCM identifies inflammatory cells (with an inter- and perifollicular distribution (square) associated with hyper/parakeratosis (arrow). d H&E staining confirms the presence of a diffuse inflammatory infiltrate.