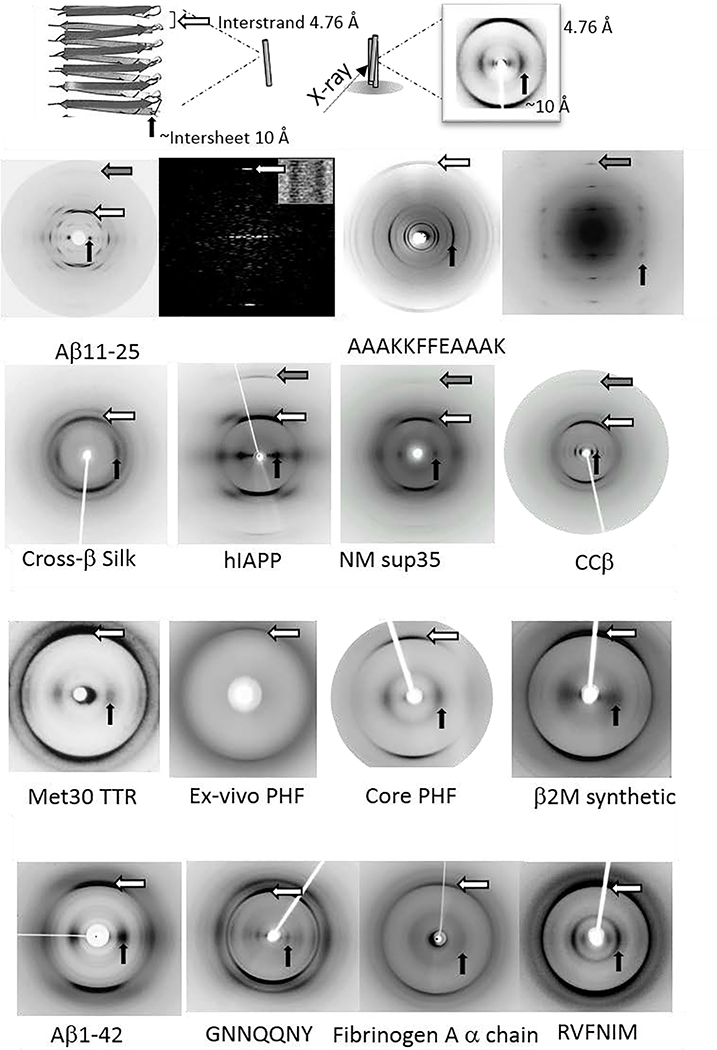
Fig. 4.
X-ray fibre diffraction provides the characteristic cross-β pattern for amyloid. Top panel shows a schematic showing the features of the cross-β pattern and structure. Lower panels show the cross-β diffraction patterns collected from amyloid fibrils formed by a diverse range of amyloidogenic proteins and peptides. Aβ11–25,72–74 AAAKKFFEAAAK,52 silk,75 hIAPP,76 NM Sup35,77 ccβ,78 Met30 TTR,79 Tau,80 Core PHF,81 β2M,82 Aβ42,73, 83 GNNQQNY,84 Fibrinogen,85 RVFNIM.86 Reproduced with permission from ref. 72, copyright 2000 The American Chemical Society.72 Reproduced with permission from ref. 73, copyright 2003 Elsevier.73 Reproduced with permission from ref. 74, copyright 2000 Elsevier.74 Reproduced with permission from ref. 52, copyright 2005 National Academy of Sciences.52 Reproduced with permission from ref. 75, copyright 2007 Wiley-VCH.75 Reproduced with permission from ref. 76, copyright 2004 Elsevier.76 Reproduced with permission from ref. 77, copyright 2000 American Association for the Advancement of Science.77 Reproduced with permission from ref. 78, copyright 2008 Elsevier.78 Reproduced with permission from ref. 79, copyright 1996 Ciba Foundation.79 Reproduced with permission from ref. 80, copyright 2003 National Academy of Sciences.80 Reproduced with permission from ref. 81, copyright 2017 Elsevier.81 Reproduced with permission from ref. 82, copyright 2008 American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology.82 Reproduced with permission from ref. 87, copyright 2012 American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology.87 Reproduced with permission from ref. 84, copyright 2010 Elsevier.84 Reproduced with permission from ref. 85, copyright 2007 Informa Healthcare.85 Reproduced with permission from ref. 86, copyright 2013 Portland Press.86