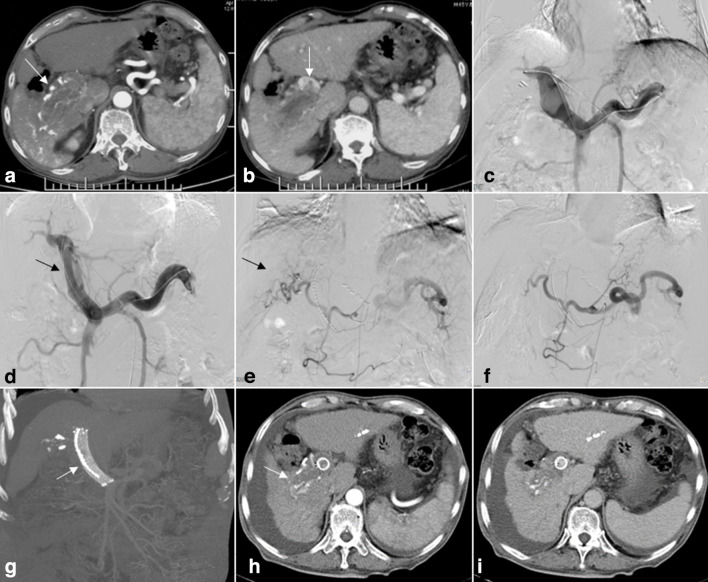
Figure 1.
A 65-year-old male who had hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) with Vp4 portal vein tumor thrombosis (PVTT). (A) Contrast-enhanced CT cross-sectional image demonstrating HCC lesions in segment 6 (arrows). (B) PVTT from the right branch of the portal vein extending to the main portal vein (arrows). (C) The left patent intrahepatic portal vein branch was punctured, portography showing an irregular filling defect at the confluence of the left portal vein and main portal trunk. The right portal vein branch is not shown. (D) Self-expandable stents and iodine-125 seed-strips were placed in the obstructed main portal vein and the posterior segment of the left intrahepatic portal vein (arrows). (E) After advancing the catheter into the feed artery, injection of contrast medium revealed the tumor. (F) Occlusion of the tumor feeding arteries following TACE. (G-I) Results from a 6-month follow-up review. Iodine-125 seed-strips fixed firmly between the PVTT and stent. Treated lesions were observed to have decreased in size, the stent exhibiting satisfactory patency (arrows).