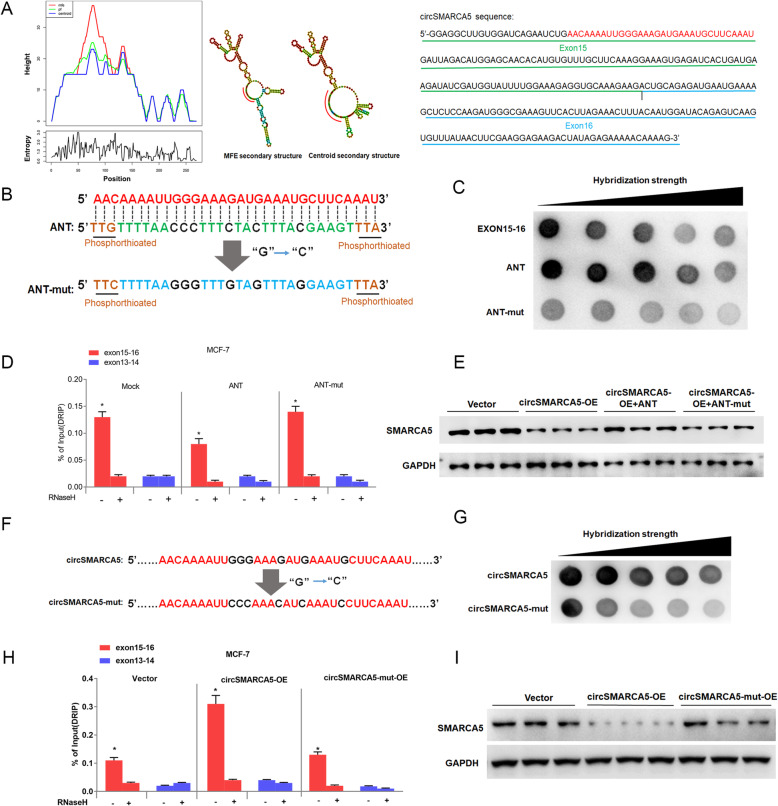
Fig. 6.
circSMARCA5 can form an R-loop with its parent gene. a Secondary structure prediction for circSMARCA5 using the Mfold program. The sequence KEY shared by the minimum free energy structure and the thermodynamic ensemble structure is marked by red. b The thiophosphorus nucleic acid analog ANT complementary to KEY and its mutant ANT-mut were synthesized in vitro. c Dot-blot verifying the interaction between circSMARCA and ANT or ANT-mut. d DRIP-qPCR analysis on 15-16 exon or 13-14 exon sequences of SMARCA5 to detect the association of circSMARCA5 in MCF-7 cells overexpressing ANT or ANT-mut, RNase H-treated and/or DRIP-qPCR analysis of the 15-16 exon sequence as a control. “*” indicates P < 0.05. e Western blot analysis shows that transfection of ANT into circSMARCA5-overexpressing cells can restore SMARCA5 protein levels but ANT-mut cannot. (f, g) Dot-blot analysis quantifying R-loop strength between the SMARCA5 locus and circSMARCA5 or circSMARCA5-mut (guanine converted to cytosine of the KEY sequence). h DRIP-qPCR in MCF-7 cells transfected with circSMARCA5 or circSMARCA5-mut. RNase H-treated genomic DNA and qPCR of exon13-14 were treated as controls. “*” indicates P < 0.05. i Western blot analysis shows that overexpression of circSMARCA5 to MCF-7 cells can decrease SMARCA5 protein levels but circSMARCA5-mut cannot