Figure 2 .
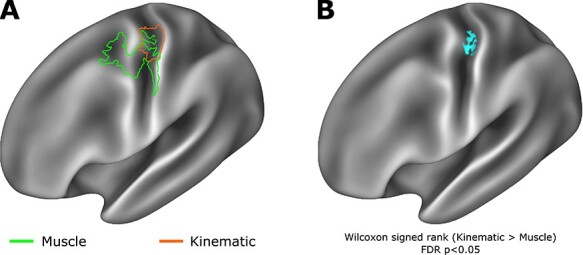
Kinematic and muscle models show evidence of distinct spatial encoding in primary motor cortex. (A) Outline of supra-threshold RSA results presented in Fig. 1 reveal overlapping but distinct encoding of muscle and kinematic information, with muscle information encoding in more rostral regions of Brodmann areas 4 and 6, while kinematic information is encoded in more caudal regions of primary motor cortex, including Brodmann areas 4 and 3a. (B) A Wilcoxon signed-rank test calculated on Spearman’s ρ values across the muscle and kinematic spatial searchlights revealed a region at the border of Brodmann areas 4 and 3a in which kinematic information showed significantly greater encoding than the muscle model (Statistical maps subject to FDR correction α = 0.05).
