FIG 3.
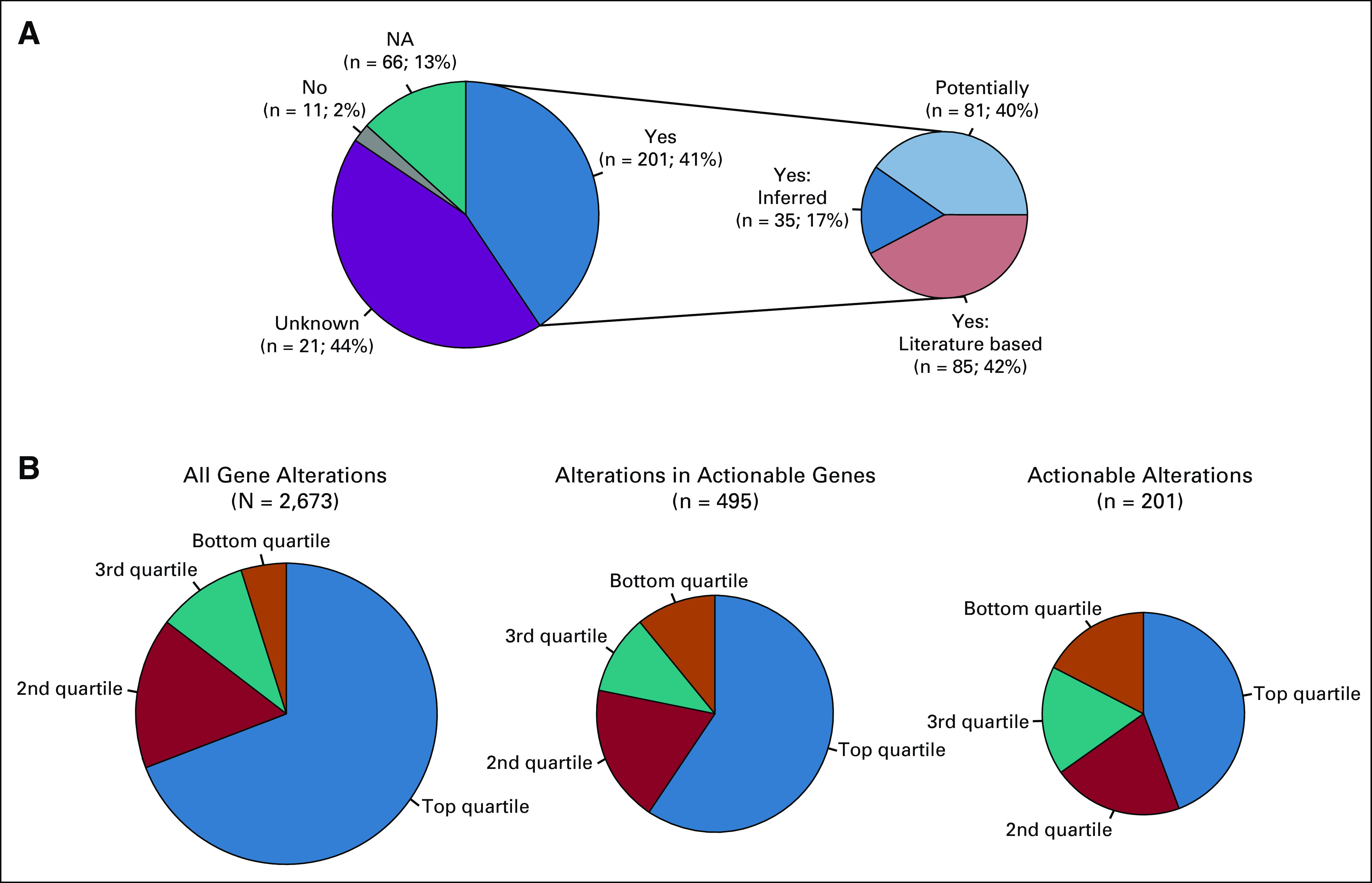
(A) Distribution of variants in actionable genes. Forty-four percent of the alterations found in actionable genes were variants of unknown significance (Unknown), and 13% were not annotated because they were all from one hypermutated patient (NA). Of the alterations with known function, 2% are known to be benign or not actionable (No), with the remainder having some annotated function on the basis of the existing literature. Functional significance was assessed on the basis of the specific variant having a reported function in the literature on the basis of the rules described in Patients and Methods. (B) Distribution of total alterations, alterations in actionable genes, and actionable alterations as organized by quartiles of patients by total mutation load. Presence of clinically actionable alterations was not related to high overall tumor mutation burden.
