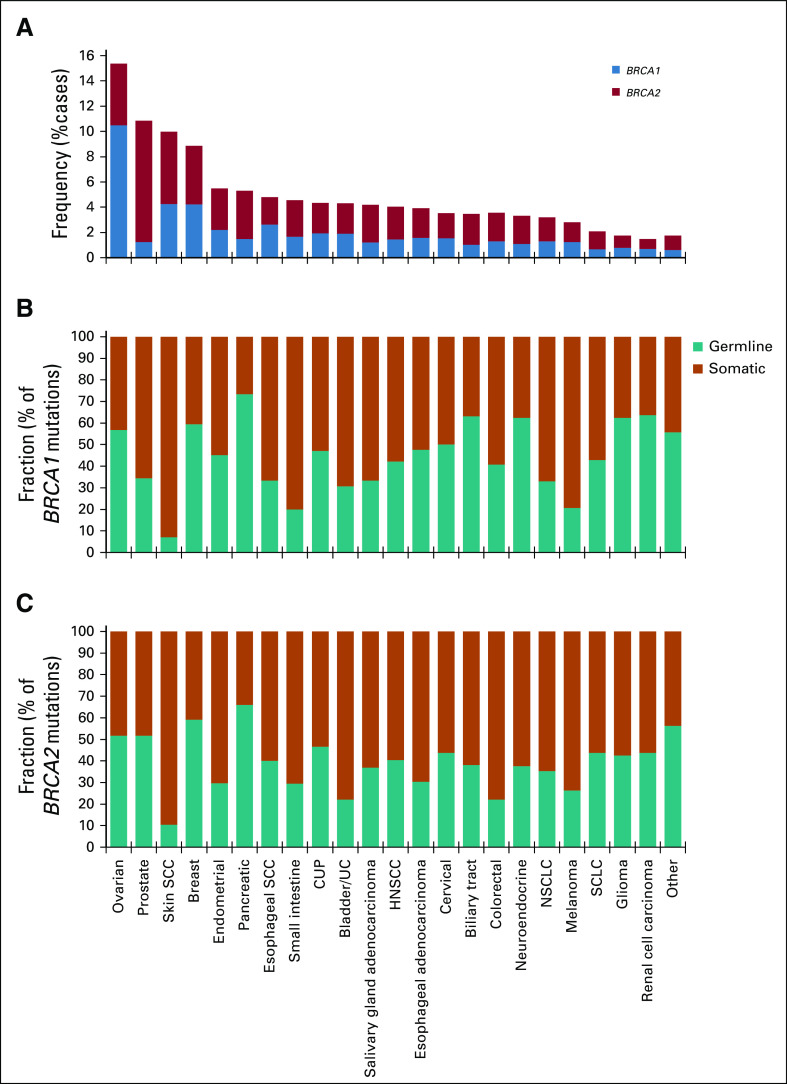
FIG 1.
Pan-cancer landscape of BRCA1/2 alterations. (A) Frequency of BRCA1 and BRCA2 alterations across multiple cancer types. Cancer types with ≥ 40 BRCA1/2-altered cases are shown, including ovarian cancer (n = 14,256), prostate cancer (n = 7,185), skin squamous cell carcinoma (SCC; n = 661), breast cancer (n = 21,164), endometrial cancer (n = 7,182), pancreatic cancer (n = 12,248), esophageal SCC (n = 836), small intestine cancer (n = 1,145), cancer of unknown primary (CUP; n = 11,130), bladder/urothelial cancer (UC; n = 4,718), salivary gland adenocarcinoma (n = 1,075), head and neck SCC (HNSCC; n = 2,921), gastric/esophageal adenocarcinoma (n = 8,061), cervical cancer (n = 1,694), biliary tract cancer (n = 6,003), colorectal cancer (n = 25,784), neuroendocrine cancer (n = 4,573), non–small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC; n = 43,242), melanoma (n = 6,016), small-cell lung cancer (SCLC; n = 2,262), glioma (n = 8,635), and renal cell carcinoma (n = 3,330); all other cancer types were analyzed as a group labeled other (n = 40,033). See the Data Supplement for detailed data. (B and C) Predicted germline/somatic status was determined computationally for BRCA1/2 short variant mutations. Fraction (%) of (B) BRCA1 or (C) BRCA2 mutations predicted to be germline v somatic was determined for each cancer type. See the Data Supplement for detailed data.