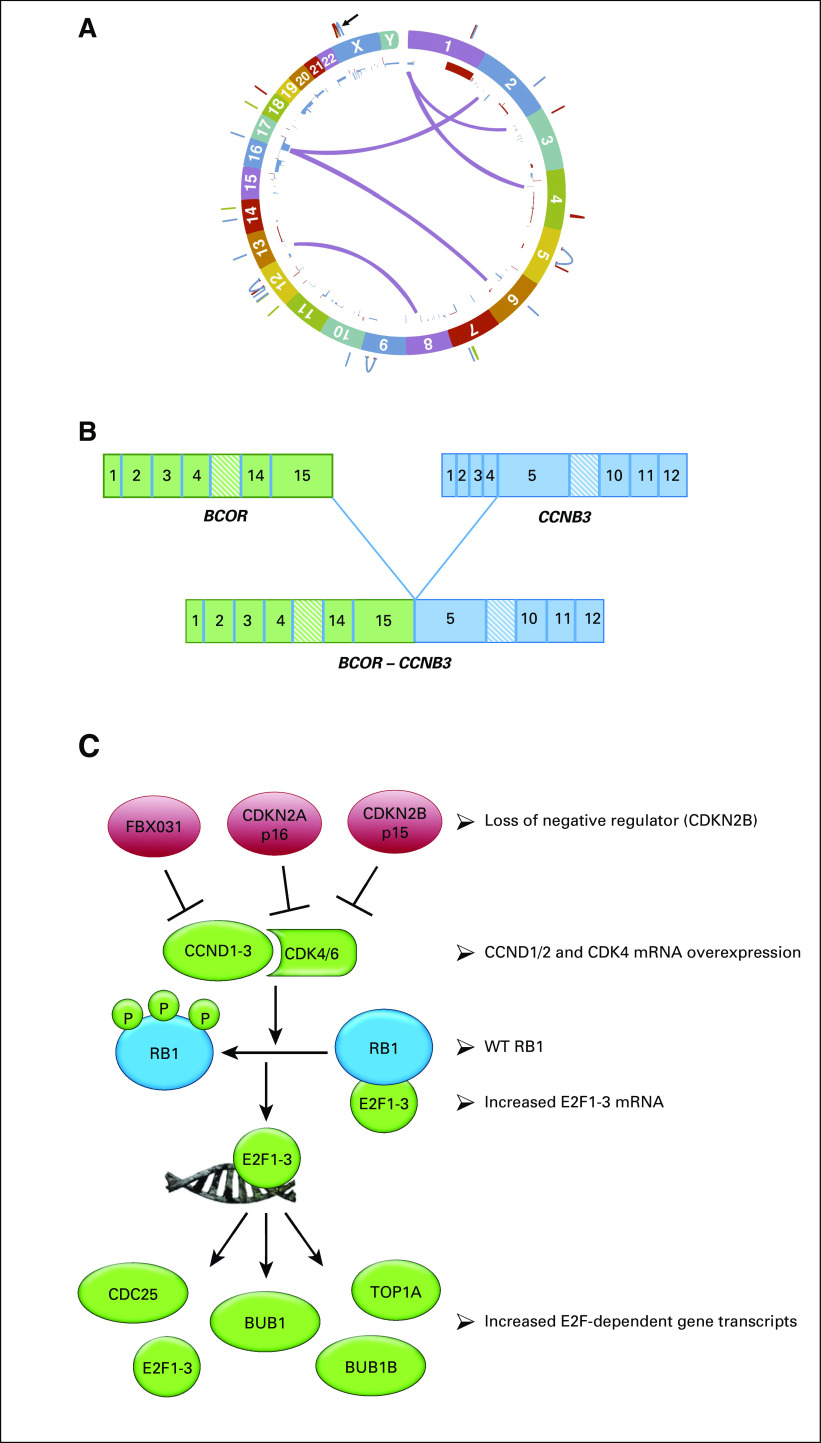
FIG 2.
Transcriptome analysis reveals activation of the cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 (CDK4/6)-RB pathway. (A) Circos plot of patient’s tumor genome. (B) Identification of BCOR-CCNB3 fusion. This graphic illustrates the fusion of BCOR exon 15 to CCNB3 exon 5. With the exception of the destruction box in CCNB3, all functional domains from each encoded protein remain intact in the BCOR-CCNB3 fusion protein. (C) The CDK4/6 pathway is a gene regulatory program controlled by multiple tiers of protein kinases and transcriptional regulators. Increases in cyclin-D or CDK4 or 6 protein can lead to phosphorylation of the RB1-E2F tumor suppressor complex. Upon phosphorylation of RB1, the E2F1-3 transcription factors are released from the complex and are able to bind to the promoters of target genes, driving activation of transcription. These target genes include E2F1-3 themselves, the CDC25 genes, TOP2A, BUB1, and BUB1B. WT, wild type.