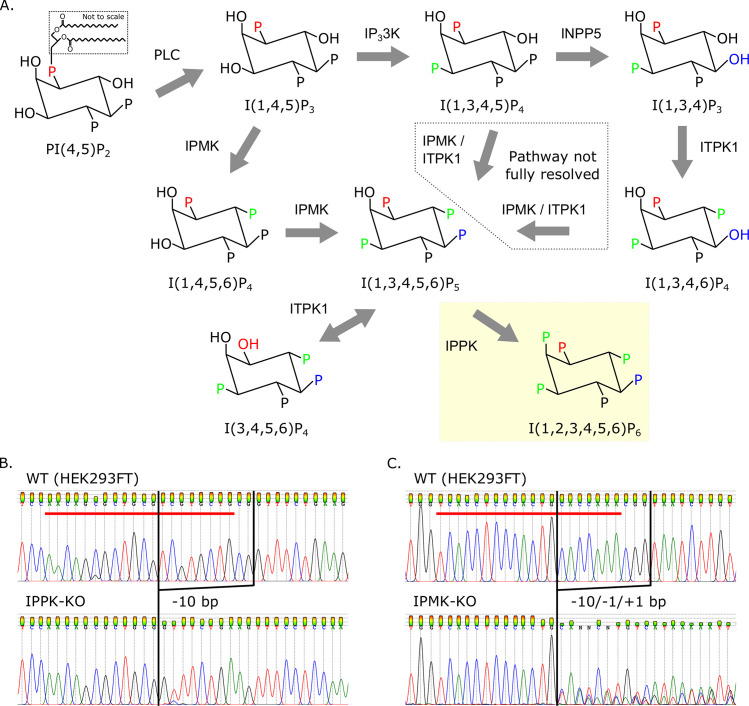
Fig 1. Knock-out of cellular genes leading to the production of IP6.
(A) Inositol phosphate pathway in H. sapiens. Inositol-pentakisphosphate 2-kinase (IPPK) adds the sixth phosphate to position 2 of IP5 (yellow box). IP5 synthesis from I(1,3,4,5)P4 and I(1,3,4,6)P4 has not been fully resolved. Other abbreviations: phospholipase C (PLC), IP33K (inositol-triphosphate 3-kinase), IPMK (inositol-polyphosphate multikinase), INPP5 (inositol-polyphosphate 5-phosphatase), and ITPK1 (inositol-tetrakisphosphate 1-kinase). (B-C) Chromatograms showing insertion-deletions of inositol-phosphate pathway KOs in HEK293FTs. Red bars delineate the 20-base pair guide RNA sequence used for CRISPR/Cas9 targeting. (B) KO of IPPK has a 10-base pair (bp) deletion. (C) KO of IPMK has three copies with 1- and 10-bp deletions and a 1-bp insertion.