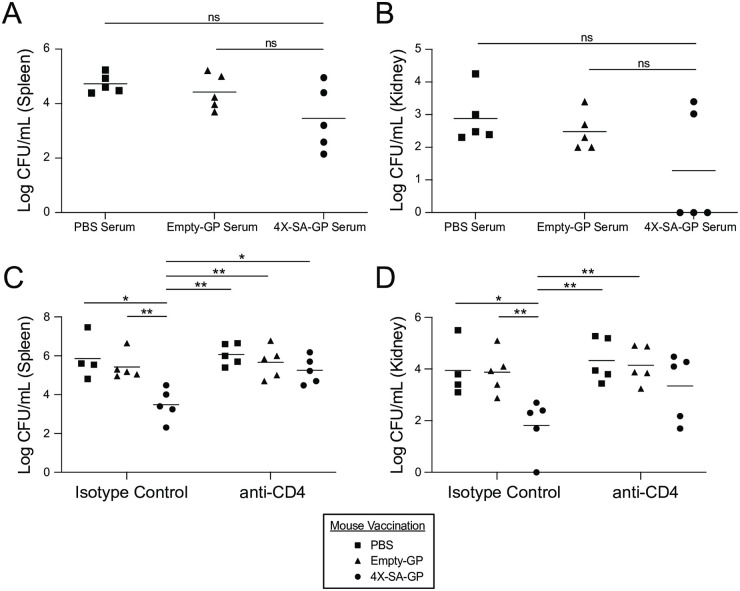
Fig 7. Antibodies alone are not sufficient to provide 4X-SA-GP-induced protection against systemic S. aureus infection, while CD4+ T cells are indispensable.
(A and B) Wild-type female mice were immunized once a week for 3 weeks with PBS, Empty-GP, or 4X-SA-GP and serum was collected from each group of mice 2 weeks after the final vaccination. The serum from each group of mice was pooled and injected i.p. into wild-type female naïve recipient mice (n = 5 mice/group, PBS serum, Empty-GP serum, 4X-SA-GP serum). The recipient mice were infected i.p. with 2x107 CFUs of S. aureus (LAC USA300) the following day. Bacteria from the spleen (A) and kidneys (B) were recovered after 24 hours and CFUs were enumerated. (C and D) Wild-type female mice were immunized once a week for 3 weeks with PBS (n = 9), Empty-GPs (n = 10), or 4X-SA-GP (n = 10). Four weeks after the final vaccination 4–5 mice per vaccination group were treated i.p. with anti-CD4+ antibody or the corresponding isotype control antibody on day -1 and day 0. On day 0, all groups of the mice were infected i.p. with 2x107 CFUs of S. aureus (LAC USA300). Bacteria from the spleen (C) and kidneys (D) were recovered after 24 hours after the S. aureus infection and CFUs were enumerated. Each data point represents an individual mouse. Data from the serum transfer is representative of two experiments. Data from the CD4+ T cell depletion is from a single experiment. Data analysis was performed using Kruskal-Wallis test ((A) = 0.18, (B) = 0.46, (C) = 0.0.02, (D) = 0.05) and Mann-Whitney U test. *p<0.05, **p<0.01; ns, not significant.