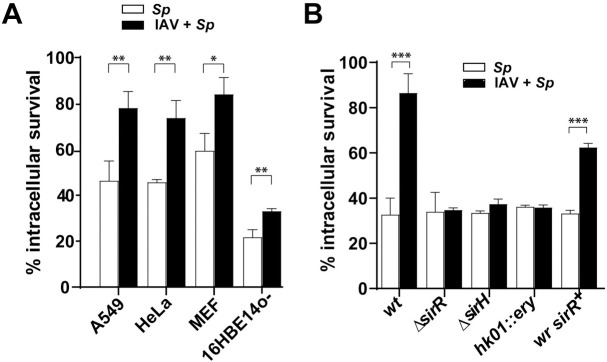
Fig 1. Enhancement of pneumococcal intracellular survival by influenza A infection is mediated by the SirRH two-component system.
(A) The IAV-S. pneumoniae synergism is independent of the cell line. The A549, MEF, 16HBE14o- and HeLa cells were treated for 24 h with a viral MOI of 10 and posteriorly infected with the pneumococcal wt strain using a bacterial MOI of 30. Bacterial survival progression was monitored using a typical protection assay. Survival percentages were calculated by considering the total amount of internalized bacteria after 30 min of extracellular antibiotic treatment as representing 100% for each strain. After antibiotic treatment, samples were taken at 4 hours, and pneumocytes were lysed to release pneumococci. Samples were diluted in BHI, spread on BHI-blood-agar plates and incubated at 37°C for 16 h. IAV-infected cells are indicated with black bars and non-virus infected cells with white bars. (B) The synergism between IAV and S. pneumoniae is mediated by the SirRH two-component system. A549 cells were previously infected with a viral MOI of 10 for 24 h, and then coinfected by the wt, ΔsirH, hk01::ery (or sirH::ery) and ΔsirR strains, and the revertant of the ΔsirR mutant (wr sirR+). Intracellular survival rates were determined as described in panel A. IAV-infected cells are indicated with black bars and non-virus infected cells with white bars. For both panels, data are representative of at least three independent experiments and statistically significant differences are indicated as p<0.05 (*), p<0.01 (**) or p<0.001 (***).