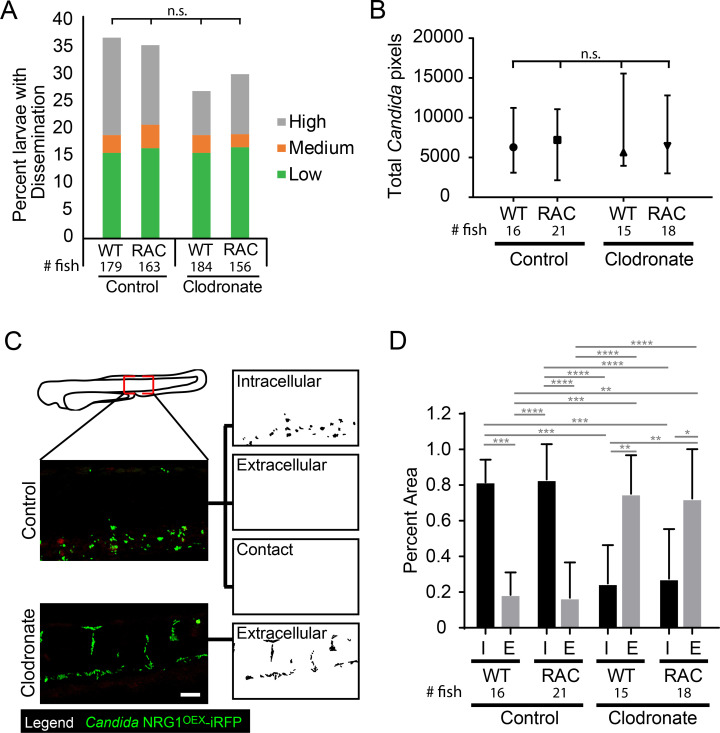
Fig 3. Phagocytes are not required for yeast dissemination to occur.
Rac2-D57N and AB sibling larvae were injected with control or clodronate liposomes mixed with a 10 kDa dextran conjugated with Cascade Blue in the caudal vein at 28 hpf. Larvae were infected with the yeast locked C. albicans 4 hours later as described above. (A) Percent infected larvae with dissemination scored as “low” (1–10), “medium” (10–50), and “high” (>50 yeast) disseminated yeast at 40 hpi. Pooled from 6 experiments. Stats: Fisher’s Exact test, n.s. not significant p>0.05 (B) Total pixel counts for quantified disseminated yeast for each group are shown with the median and interquartile range. Same larvae as in Panels C & D. (C) Method used to quantify disseminated yeast. Yeast were scored as Intracellular (I; inside or in close contact with a phagocyte) or Extracellular (E; not contained or in contact with phagocytes). Images were processed in ImageJ. Scale bar = 50 μm. (D) The proportion of all yeast either Intracellular or Extracellular for each treatment group. Stats: Kruskall-Wallis with Dunn’s posttest (* p≤ 0.05, ** p ≤ 0.01, *** p ≤ 0.001, **** p < 0.0001), and bars indicate the median with interquartile range. Pooled from 6 experiments. Stats: Kruskall-Wallis with Dunn’s post-test. All comparisons were n.s.