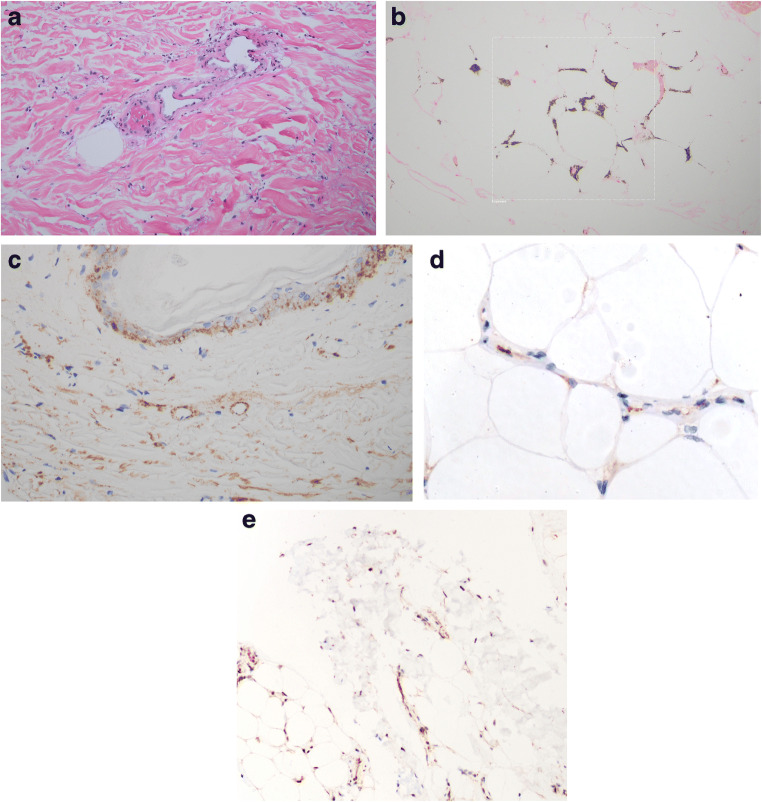
Fig. 3.
In situ deposition of components of complement activation (C3d, C4d, C5b-9, and MASP2). Assays were conducted on 4 μm sections procured from formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue. Immunohistochemical assessment of SARS-CoV-2 associated envelope protein and ACE2 receptor expression was also conducted. A pauci-inflammatory thrombogenic vasculopathy was present throughout the dermis (a) and subcutaneous fat (hematoxylin and eosin, × 400). A Von Kassa preparation confirmed the presence of calcium within the subcutaneous microvasculature (b) (Von Kassa, × 400). A critical role for complement activation in the pathogenesis of the thrombotic alterations was revealed by the extent of C4d and C5b-9 deposition. Illustrated are granular deposits of C5-9 within the microvasculature of the dermis (c) (diaminobenzidene, × 400). Endothelial viral microparticles were confirmed via immunohistochemical assessment for the presence of SARS-CoV-2 envelope protein (primary antibodies from ProSci Poway, CA at 1:500 dilution, × 200) (d) as well as ACE2 receptor (primary antibodies from Proteintech at a 1:13,000 dilution, × 1000) (e) within the deep dermis and subcutaneous fat