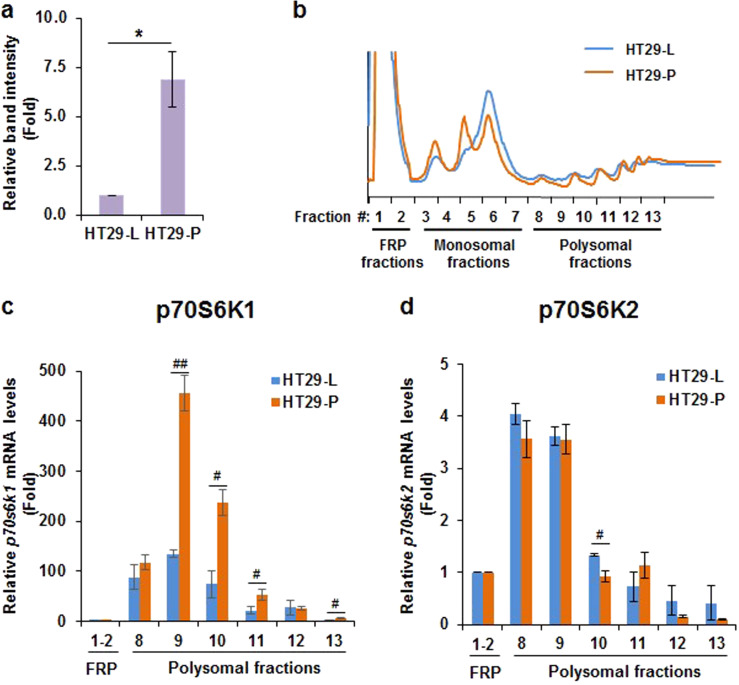
Fig. 3.
Knockdown of Pdcd4 enhances p70S6K1 translation. a p70S6K1 protein levels were increased in Pdcd4 knockdown cells. The level of p70S6K1 in control (HT29-L) and Pdcd4 knockdown (HT29-P) cells at 0 h treatment in Fig. 2a was quantified. The band intensity of p70S6K1/GAPDH in HT29-L cells is designated as 1. Data from three independent experiments were analyzed by one-sample t-test (mean ± SD; *P < 0.05). b Polysomal profiles of HT29-L and HT29-P cells. Pdcd4 knockdown increases p70s6k1 mRNA (c) but not p70s6k2 mRNA (d) in polysomal fractions. The cell lysates from HT29-L and HT29-P cells were subjected to sucrose gradient fractionation. After fractionation, the mRNAs in each fraction were purified and quantified with RT-qPCR. RT-qPCR was performed with three replicates to determine the relative levels of p70S6K1 or p70S6K2 mRNA by comparison of p70S6K1 or p70S6K2 mRNA in each polysomal fraction to that in corresponding pooled free RNAs and proteins (FRP) fraction, respectively. Data from two independent experiments were analyzed by two-sample t-test (mean ± SD; #P < 0.05; ##P < 0.01)